 |
| July 06, 2021 | Volume 17 Issue 25 |
Mechanical News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
How ball spline coatings enhance performance and extend component life
 According to Thomson, "Precision ball splines have gained popularity as an ideal choice for applications that require low-friction linear and rotary motion. These components, which utilize a single splined shaft, enable complex movements in multiple directions." But how do you keep these ball splines performing at their peak for longer? Coatings can do the trick, and Thomson has three of them: black oxide, hard chrome plating, and nickel plating. Learn more about these coatings and which one makes the most sense for your precision ball spline solution.
According to Thomson, "Precision ball splines have gained popularity as an ideal choice for applications that require low-friction linear and rotary motion. These components, which utilize a single splined shaft, enable complex movements in multiple directions." But how do you keep these ball splines performing at their peak for longer? Coatings can do the trick, and Thomson has three of them: black oxide, hard chrome plating, and nickel plating. Learn more about these coatings and which one makes the most sense for your precision ball spline solution.
View the video.
Key factors for ball screw applications
 Learn the six key factors that should be considered when specifying ball screw assemblies in motion control applications. PCB Linear gathered a panel of experts in the field of linear motion to concentrate on this important topic -- particularly when it comes to the company's new miniature ball screw product line. Learn about precision and accuracy, orientation, speed and acceleration, duty cycle, linear motion travel, and load capacity. Podcast available too.
Learn the six key factors that should be considered when specifying ball screw assemblies in motion control applications. PCB Linear gathered a panel of experts in the field of linear motion to concentrate on this important topic -- particularly when it comes to the company's new miniature ball screw product line. Learn about precision and accuracy, orientation, speed and acceleration, duty cycle, linear motion travel, and load capacity. Podcast available too.
Read the PCB Linear blog.
3D printer uses pellet extrusion system instead of filament
 The latest addition to 3D Systems' industry-leading portfolio of EXT Titan Pellet systems is the EXT 800 Titan Pellet. With a build volume of 800 x 600 x 800 mm, this thermoplastics 3D printer harnesses the speed, reliability, and efficiency of the company's large-format pellet systems in a more compact unit with lower upfront investment. Use this machine to fabricate more modestly sized functional prototypes, tooling, fixtures, sand casting patterns, thermoforming molds, and end-use parts. Markedly faster than competing FFF and FDM printers, and up to 10X reduced material costs compared to filaments.
The latest addition to 3D Systems' industry-leading portfolio of EXT Titan Pellet systems is the EXT 800 Titan Pellet. With a build volume of 800 x 600 x 800 mm, this thermoplastics 3D printer harnesses the speed, reliability, and efficiency of the company's large-format pellet systems in a more compact unit with lower upfront investment. Use this machine to fabricate more modestly sized functional prototypes, tooling, fixtures, sand casting patterns, thermoforming molds, and end-use parts. Markedly faster than competing FFF and FDM printers, and up to 10X reduced material costs compared to filaments.
Learn more.
Test your knowledge: High-temp adhesives
 Put your knowledge to the test by trying to answer these key questions on how to choose the right high-temperature-resistant adhesive. The technical experts from Master Bond cover critical information necessary for the selection process, including questions on glass transition temperature and service temperature range. Some of the answers may surprise even the savviest of engineers.
Put your knowledge to the test by trying to answer these key questions on how to choose the right high-temperature-resistant adhesive. The technical experts from Master Bond cover critical information necessary for the selection process, including questions on glass transition temperature and service temperature range. Some of the answers may surprise even the savviest of engineers.
Take the quiz.
World's first current-carrying fastening technology
 PEM® eConnect™ current-carrying pins from Penn-Engineering provide superior electrical connections in applications that demand high performance from internal components, such as automotive electronics. This first-to-market tech provides repeatable, consistent electrical joints and superior installation unmatched by traditional fastening methods. Features include quick and secure automated installation, no hot spots or poor conductivity, and captivation options that include self-clinching and broaching styles.
PEM® eConnect™ current-carrying pins from Penn-Engineering provide superior electrical connections in applications that demand high performance from internal components, such as automotive electronics. This first-to-market tech provides repeatable, consistent electrical joints and superior installation unmatched by traditional fastening methods. Features include quick and secure automated installation, no hot spots or poor conductivity, and captivation options that include self-clinching and broaching styles.
Learn more about eConnect pins.
New flat quarter-turn clamping fastener
 IMAO Fixtureworks has expanded its One-Touch Fastener lineup to include a new quarter-turn clamping fastener that features an innovative flat design and is ideal for clamping in limited spaces. The QCFC flat quarter-turn fastener features a recessed body that protrudes only 2 mm from the mounted surface, a knob that rests flush inside the body, visible ON and OFF markings for safety, and an audible click when fully turned to clamped or unclamped position.
IMAO Fixtureworks has expanded its One-Touch Fastener lineup to include a new quarter-turn clamping fastener that features an innovative flat design and is ideal for clamping in limited spaces. The QCFC flat quarter-turn fastener features a recessed body that protrudes only 2 mm from the mounted surface, a knob that rests flush inside the body, visible ON and OFF markings for safety, and an audible click when fully turned to clamped or unclamped position.
Learn more.
Bellows and disc couplings with higher torque capacity
 Ruland Manufacturing now offers bellows and double disc couplings with bore sizes up to 1-3/4 in. or 45 mm for use in systems with torque up to 1,400 in.-lb (158 Nm). High-torque applications in precision semiconductor, solar, conveyor, and factory automation applications often use these shaft sizes. Ruland disc and bellows couplings accommodate all forms of misalignment, are zero-backlash, and have a balanced design for reduced vibration at speeds up to 10,000 rpm.
Ruland Manufacturing now offers bellows and double disc couplings with bore sizes up to 1-3/4 in. or 45 mm for use in systems with torque up to 1,400 in.-lb (158 Nm). High-torque applications in precision semiconductor, solar, conveyor, and factory automation applications often use these shaft sizes. Ruland disc and bellows couplings accommodate all forms of misalignment, are zero-backlash, and have a balanced design for reduced vibration at speeds up to 10,000 rpm.
Learn more.
Simplify your designs with slewing ring bearings
 According to Kaydon Bearings, "A slewing ring bearing has rolling elements designed to create a reactive moment within the bearing's dimensions envelope to oppose applied (overturning) moment load," so you can use one bearing instead of two, reducing the height requirements, and even improve performance. Slewing ring bearings can also simplify a drive system by utilizing gear teeth on the inner or outer race. Learn all about slewing ring bearings in this informative article.
According to Kaydon Bearings, "A slewing ring bearing has rolling elements designed to create a reactive moment within the bearing's dimensions envelope to oppose applied (overturning) moment load," so you can use one bearing instead of two, reducing the height requirements, and even improve performance. Slewing ring bearings can also simplify a drive system by utilizing gear teeth on the inner or outer race. Learn all about slewing ring bearings in this informative article.
Read the Kaydon whitepaper.
Jet valve for ultra-small dispensing
 DELO's DELO-DOT PN5 LV pneumatic jet valve is designed for micro-dispensing low-viscosity adhesives and other media in miniaturized applications. Thanks to its compact design, it also requires very little space to install in production systems. Interchangeable nozzles with different diameters and a flexible, adjustable plunger stroke ensure precise and reliable applications at different droplet sizes. Volumes of as low as 1 nl can be achieved, which corresponds to droplet diameters of 250 µm or less.
DELO's DELO-DOT PN5 LV pneumatic jet valve is designed for micro-dispensing low-viscosity adhesives and other media in miniaturized applications. Thanks to its compact design, it also requires very little space to install in production systems. Interchangeable nozzles with different diameters and a flexible, adjustable plunger stroke ensure precise and reliable applications at different droplet sizes. Volumes of as low as 1 nl can be achieved, which corresponds to droplet diameters of 250 µm or less.
Learn more.
Stainless steel constant-torque flush-mount hinge
 Southco has introduced a flush-mount version of its popular and durable E6 constant-torque hinge. Its low-profile, corrosion-resistant package makes it an ideal solution for maximizing security, longevity, and aesthetics. It offers high torque for demanding applications while maintaining its low profile. Lots of uses.
Southco has introduced a flush-mount version of its popular and durable E6 constant-torque hinge. Its low-profile, corrosion-resistant package makes it an ideal solution for maximizing security, longevity, and aesthetics. It offers high torque for demanding applications while maintaining its low profile. Lots of uses.
Learn more.
Claw vacuum pump for industrial applications
 Vacuum expert Leybold has added a new model to its proven CLAWVAC dry claw vacuum pump series: the CLAWVAC CP B. This innovative, rough vacuum pump, designed for robust processes including food processing, material handling, and environmental industries, is powerful, energy efficient, and easy to clean. The intuitive handling of this unit is mainly due to its functional design, which features a pair of claws that rotate in the cylinder with no contact or wear. Its separate gearbox prevents oil contamination. The design ensures short downtimes and long service intervals: 20,000 hr between oil changes and up to 48,000 hr between general overhauls.
Vacuum expert Leybold has added a new model to its proven CLAWVAC dry claw vacuum pump series: the CLAWVAC CP B. This innovative, rough vacuum pump, designed for robust processes including food processing, material handling, and environmental industries, is powerful, energy efficient, and easy to clean. The intuitive handling of this unit is mainly due to its functional design, which features a pair of claws that rotate in the cylinder with no contact or wear. Its separate gearbox prevents oil contamination. The design ensures short downtimes and long service intervals: 20,000 hr between oil changes and up to 48,000 hr between general overhauls.
Learn more.
DualVee linear guides and tracks used in warehousing
 See how Bishop-Wisecarver's DualVee® motion tech can add huge benefits to warehousing operations. This video highlights two applications: a manual storage and retrieval system and an automated storage and retrieval system of long aerospace-grade carbon fiber in sub-zero temps. Patented DualVee guides and tracks keep operations running smoothly.
See how Bishop-Wisecarver's DualVee® motion tech can add huge benefits to warehousing operations. This video highlights two applications: a manual storage and retrieval system and an automated storage and retrieval system of long aerospace-grade carbon fiber in sub-zero temps. Patented DualVee guides and tracks keep operations running smoothly.
View the video.
Build-to-order knobs and hand hardware
 Rogan Corp.'s innovative use of two-shot plastic injection and insert molding has been providing customers with high-quality plastic clamping knobs, levers, and control knobs for almost 90 years. Rogan offers concurrent engineering, product design, and assistance in material selection to ensure customer satisfaction for standard or customized parts, with a focus on cost optimization and on-time delivery. Custom colors, markings, decorative inlays, or engineered materials to meet special requirements, such as adding extra strength or utilizing flame-retardant material, are all offered.
Rogan Corp.'s innovative use of two-shot plastic injection and insert molding has been providing customers with high-quality plastic clamping knobs, levers, and control knobs for almost 90 years. Rogan offers concurrent engineering, product design, and assistance in material selection to ensure customer satisfaction for standard or customized parts, with a focus on cost optimization and on-time delivery. Custom colors, markings, decorative inlays, or engineered materials to meet special requirements, such as adding extra strength or utilizing flame-retardant material, are all offered.
Learn more.
Slewing ring bearing made of wood and plastic
 The PRT-02-30-WPC slewing ring bearing is another step forward by igus toward integrating renewable raw materials into industrial production. Made of 50% wood and 50% high-performance plastics, the cost-effective and lubrication-free slewing ring bearing balances strength and durability with a proven low CO2 footprint. The materials incorporate solid lubricants, making the new slewing ring bearing smooth running and maintenance-free.
The PRT-02-30-WPC slewing ring bearing is another step forward by igus toward integrating renewable raw materials into industrial production. Made of 50% wood and 50% high-performance plastics, the cost-effective and lubrication-free slewing ring bearing balances strength and durability with a proven low CO2 footprint. The materials incorporate solid lubricants, making the new slewing ring bearing smooth running and maintenance-free.
Learn more.
Flex Locators for quick fixture changeover
 Flex Locators from Fixtureworks are designed for quick changeover of small and large fixtures, automation components, and more. They are ideal for applications that require frequent disassembly, providing excellent repeatability for locating and clamping in a single operation. Manual and pneumatic versions are available. Just turn the handle, knob, or screw!
Flex Locators from Fixtureworks are designed for quick changeover of small and large fixtures, automation components, and more. They are ideal for applications that require frequent disassembly, providing excellent repeatability for locating and clamping in a single operation. Manual and pneumatic versions are available. Just turn the handle, knob, or screw!
View the video.
Researchers make nanodiamonds and graphene in a flash
Diamond may be just a phase carbon goes through when exposed to a flash of heat, but that makes it far easier to obtain.
The Rice University lab of chemist James Tour is now able to "evolve" carbon through phases that include valuable nanodiamond by tightly controlling the flash Joule heating process they developed 18 months ago.
Best of all, they can stop the process at will to get the product they want.
In the American Chemical Society journal ACS Nano, the researchers led by Tour and graduate student and lead author Weiyin Chen show that adding organic fluorine compounds and fluoride precursors to elemental carbon black turns it into several hard-to-get allotropes when flashed, including fluorinated nanodiamonds, fluorinated turbostratic graphene, and fluorinated concentric carbon.
With the flash process introduced in 2020, a strong jolt of electricity can turn carbon from just about any source into layers of pristine turbostratic graphene in less than a second. ("Turbostratic" means the layers are not strongly bound to each other, making them easier to separate in a solution.)
The new work shows it's possible to modify, or functionalize, the products at the same time. The duration of the flash, between 10 and 500 milliseconds, determines the final carbon allotrope.
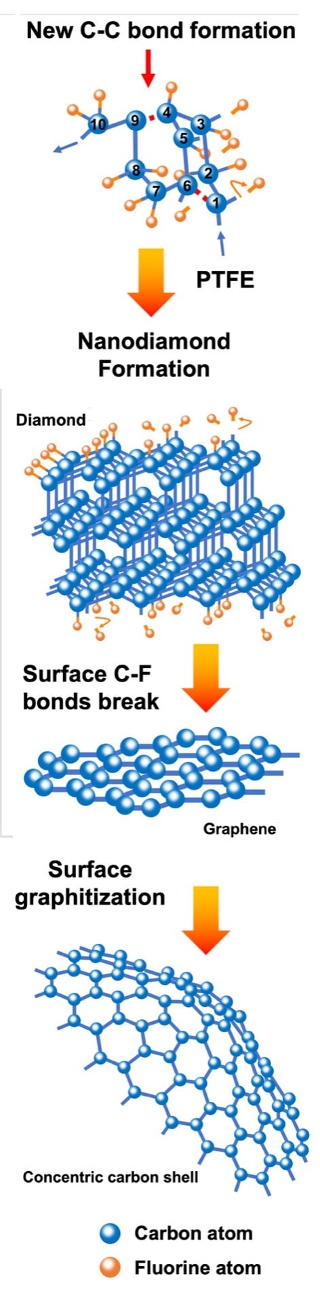
The mechanism used by Rice University chemists for the phase evolution of fluorinated flash nanocarbons shows stages with longer and larger energy input. Carbon and fluorine atoms first form a diamond lattice, then graphene, and finally polyhedral concentric carbon. [Credit: Illustration by Weiyin Chen]
The difficulty lies in how to preserve the fluorine atoms, since the ultrahigh temperature causes the volatilization of all atoms other than carbon.
To overcome the problem, the team used a Teflon tube sealed with graphite spacers and high-melting-point tungsten rods, which can hold the reactant inside and avoid the loss of fluorine atoms under the ultrahigh temperature. The improved sealed tube is important, Tour said.
"In industry, there has been a long-standing use for small diamonds in cutting tools and as electrical insulators," he said. "The fluorinated version here provides a route to modifications of these structures. And there is a large demand for graphene, while the fluorinated family is newly produced here in bulk form."
Nanodiamonds are microscopic crystals -- or regions of crystals -- that display the same carbon-atom lattice that macro-scale diamonds do. When first discovered in the 1960s, they were made under heat and high pressure from detonations.
In recent years, researchers have found chemical processes to create the same lattices. A report from Rice theorist Boris Yakobson last year showed how fluorine can help make nanodiamond without high pressure, and Tour's own lab demonstrated using pulsed lasers to turn Teflon into fluorinated nanodiamond.
Nanodiamonds are highly desirable for electronics applications, as they can be doped to serve as wide-bandgap semiconductors, important components in current research by Rice and the Army Research Laboratory.
The new process simplifies the doping part, not only for nanodiamonds but also for the other allotropes. Tour said the Rice lab is exploring the use of boron, phosphorous, and nitrogen as additives as well.
At longer flash times, the researchers got nanodiamonds embedded in concentric shells of fluorinated carbon. Even longer exposure converted the diamond entirely into shells, from the outside in.
"The concentric-shelled structures have been used as lubricant additives, and this flash method might provide an inexpensive and fast route to these formations," Tour said.
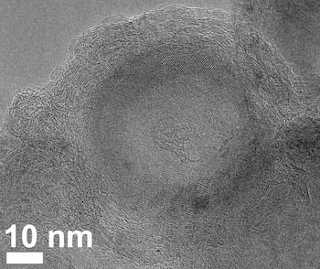
An electron microscope image shows a late stage in the evolution of carbon and fluorine atoms under flash Joule heating. The carbon atoms form concentric shells around a nanodiamond core. As heating proceeds, the diamond phase is replaced by the shell. [Credit: Courtesy of the Tour Group]
Co-authors of the paper are Rice graduate students John Tianci Li, Zhe Wang, Wala Algozeeb, Emily McHugh, Kevin Wyss, Paul Advincula, Jacob Beckham and Bo Jiang, research scientist Carter Kittrell, and alumni Duy Xuan Luong and Michael Stanford. Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice.
The Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the Department of Energy supported the research.
Source: Rice University
Published July 2021
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

