 |
| March 22, 2022 | Volume 18 Issue 12 |
Motion Control News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Robots think and act on the fly at moving assembly line speeds
 Inbolt and FANUC are launching a manufacturing breakthrough enabling FANUC robots to tackle one of the most complex automation challenges: performing production tasks on continuously moving parts at line speeds. With Inbolt's AI-powered 3D vision, manufacturers can now automate screw insertion, bolt rundown, glue application, and other high-precision tasks on parts moving down the line without costly infrastructure investments or cycle time compromises.
Inbolt and FANUC are launching a manufacturing breakthrough enabling FANUC robots to tackle one of the most complex automation challenges: performing production tasks on continuously moving parts at line speeds. With Inbolt's AI-powered 3D vision, manufacturers can now automate screw insertion, bolt rundown, glue application, and other high-precision tasks on parts moving down the line without costly infrastructure investments or cycle time compromises.
Learn more.
Best high-speed rotary bearing in THK history
 THK has developed its best-performing, high-speed rotary bearing ever: the High-Speed, Double-Row Angular Contact Ring BWH. This rotary bearing has balls aligned inside a cage between the inner and outer rings and is part of the THK Rotary Series, along with the cross-roller ring. The main features of this product are its ability to receive loads in all directions as well as its high rigidity and rotational accuracy, which are equal to that of cross-roller rings. By adopting a new structure to change the rolling elements from rollers to balls, this product achieves the greatest high-speed performance ever offered by THK.
THK has developed its best-performing, high-speed rotary bearing ever: the High-Speed, Double-Row Angular Contact Ring BWH. This rotary bearing has balls aligned inside a cage between the inner and outer rings and is part of the THK Rotary Series, along with the cross-roller ring. The main features of this product are its ability to receive loads in all directions as well as its high rigidity and rotational accuracy, which are equal to that of cross-roller rings. By adopting a new structure to change the rolling elements from rollers to balls, this product achieves the greatest high-speed performance ever offered by THK.
Learn more.
Elevating tables: Precise vertical positioning in tight spaces
 As semicon-ductors and optical components become smaller and more sophisticated, the TZ Series of precision elevating tables from IKO International provides exceptional vertical positioning accuracy in a compact size. This unit features a unique wedge mechanism guided in the vertical direction by a pair of IKO C-Lube Super MX linear motion rolling guides arranged in parallel to achieve highly precise positioning with exceptional rigidity. An optional linear encoder provides full closed loop control to achieve positioning accuracy as high as 0.005 mm, with repeatability of +/-0.001 mm.
As semicon-ductors and optical components become smaller and more sophisticated, the TZ Series of precision elevating tables from IKO International provides exceptional vertical positioning accuracy in a compact size. This unit features a unique wedge mechanism guided in the vertical direction by a pair of IKO C-Lube Super MX linear motion rolling guides arranged in parallel to achieve highly precise positioning with exceptional rigidity. An optional linear encoder provides full closed loop control to achieve positioning accuracy as high as 0.005 mm, with repeatability of +/-0.001 mm.
Learn more and get all the specs.
This cobot is all about safety around people
 The COBOTTA PRO from DENSO Robotics is a lightweight, high-speed collaborative robot designed for communication between workers and robots while maximizing productivity. It delivers a blend of productivity and safety for both simple tasks and multi-step processes like assembly and inspection work. The 6-axis unit operates at speeds up to 2,500 mm per sec when no workers are near and slows or stops when people approach. Two models available: PRO 900 (max payload 6 kg) and PRO 1300 (max payload 12 kg). Many more functions and features.
The COBOTTA PRO from DENSO Robotics is a lightweight, high-speed collaborative robot designed for communication between workers and robots while maximizing productivity. It delivers a blend of productivity and safety for both simple tasks and multi-step processes like assembly and inspection work. The 6-axis unit operates at speeds up to 2,500 mm per sec when no workers are near and slows or stops when people approach. Two models available: PRO 900 (max payload 6 kg) and PRO 1300 (max payload 12 kg). Many more functions and features.
Learn more.
Powerful, pull-type clapper solenoids handle myriad jobs
 New powerful, low-profile, pull-type clapper solenoids are available from Magnetic Sensor Systems (MSS). Applications include valve control, locks, starters, ventilators, clamping, sorting, appliances, tools, HVAC, brakes, clutches, switches, mixing, fire suppression systems, door controls, detent latches, and more. The S-16-264 Series of 17 Pull-Type Clapper Solenoids have ampere turns (windings) adjusted to meet the specific force and duty cycle requirements of your application. They provide up to 130 lb (578 N) of force.
New powerful, low-profile, pull-type clapper solenoids are available from Magnetic Sensor Systems (MSS). Applications include valve control, locks, starters, ventilators, clamping, sorting, appliances, tools, HVAC, brakes, clutches, switches, mixing, fire suppression systems, door controls, detent latches, and more. The S-16-264 Series of 17 Pull-Type Clapper Solenoids have ampere turns (windings) adjusted to meet the specific force and duty cycle requirements of your application. They provide up to 130 lb (578 N) of force.
Get all the specs for these solenoids and other options.
Tech Tip: Belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator?
 Bishop-Wisecarver provides a quick, very useful guide to help you evaluate the right drive strategy for your system: belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator. Each drive type has unique advantages and limitations, so evaluating all your options will help you find the most suitable actuator setup for your specific application needs.
Bishop-Wisecarver provides a quick, very useful guide to help you evaluate the right drive strategy for your system: belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator. Each drive type has unique advantages and limitations, so evaluating all your options will help you find the most suitable actuator setup for your specific application needs.
Read the Bishop-Wisecarver blog.
Ultra-precise linear stage -- down to 0.005 microns
 PI, a global leader in precision motion control and nanoposi-tioning, now offers fast delivery of the L-511 linear micropositioning stage, which is designed for applications requiring minimum incremental motion down to 20 nm, drive forces up to 22 lb, and multi-axis configuration options. The L-511 can be combined to form XY or XYZ motion systems and integrated with rotary stages. A variety of drive and encoder options (stepper and servo motors, rotary, and linear encoders) enable ultra-fine sensitivity. Applications include: metrology, laser processing, semiconductors, biotech, optical alignment, and advanced automation.
PI, a global leader in precision motion control and nanoposi-tioning, now offers fast delivery of the L-511 linear micropositioning stage, which is designed for applications requiring minimum incremental motion down to 20 nm, drive forces up to 22 lb, and multi-axis configuration options. The L-511 can be combined to form XY or XYZ motion systems and integrated with rotary stages. A variety of drive and encoder options (stepper and servo motors, rotary, and linear encoders) enable ultra-fine sensitivity. Applications include: metrology, laser processing, semiconductors, biotech, optical alignment, and advanced automation.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Choosing the right stepper motor: PM or hybrid?
 According to the experts at Lin Engineering, there are two primary types of stepper motors to consider: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. But which is right for your application? Both types have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific requirements.
According to the experts at Lin Engineering, there are two primary types of stepper motors to consider: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. But which is right for your application? Both types have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific requirements.
Read this informative Lin Engineering article.
New PTFE-free linear guide for precise positioning
 The new drylin WWP linear guide from igus features a PTFE-free locking carriage. Engineered from lubrication-free, high-performance polymers and aluminum, the guide offers a lightweight, hygienic, and low-maintenance alternative to complex mechanical and electronic adjustment systems. It is significantly more compact and lightweight than conventional recirculating ball-bearing systems. Applications include interior components in vehicles, aircraft, and furniture.
The new drylin WWP linear guide from igus features a PTFE-free locking carriage. Engineered from lubrication-free, high-performance polymers and aluminum, the guide offers a lightweight, hygienic, and low-maintenance alternative to complex mechanical and electronic adjustment systems. It is significantly more compact and lightweight than conventional recirculating ball-bearing systems. Applications include interior components in vehicles, aircraft, and furniture.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Heavy-duty gear units for mixing and agitating systems
 MAXXDRIVE industrial gear units from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS are an established drive solution for heavy-duty applications. In addition to conveying, lifting, and driving, they also play an important role in mixing and agitating systems. MAXXDRIVE units feature a compact, one-piece UNICASE housing that delivers long service life, easy maintenance, and quiet operation. Their robust design handles high axial and radial loads, achieves output torques up to 2,495,900 lb-in., and powers up to 8,075 hp.
MAXXDRIVE industrial gear units from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS are an established drive solution for heavy-duty applications. In addition to conveying, lifting, and driving, they also play an important role in mixing and agitating systems. MAXXDRIVE units feature a compact, one-piece UNICASE housing that delivers long service life, easy maintenance, and quiet operation. Their robust design handles high axial and radial loads, achieves output torques up to 2,495,900 lb-in., and powers up to 8,075 hp.
Learn more.
What are non-captive linear actuators?
 According to PBC Linear, their new non-captive linear actuators are different from the more common external versions of lead screw-driven linear actuators because they allow the lead screw to completely pass through the motor. This fundamental difference offers advantages for designs that have limited space available or for engineers looking to shrink the overall size of their design package.
According to PBC Linear, their new non-captive linear actuators are different from the more common external versions of lead screw-driven linear actuators because they allow the lead screw to completely pass through the motor. This fundamental difference offers advantages for designs that have limited space available or for engineers looking to shrink the overall size of their design package.
Read the full PBC Linear blog.
Güdel introduces Swiss-quality tracks for cobots
 Güdel Inc. is highlighting new technologies at Automate 2025 booth #2418 that demonstrate its unmatched ability to solve automation engineering challenges. One is the Cobomover, a 7th-axis linear track purpose-built for collaborative and lightweight robots. Designed and manufactured in Switzerland, this unit extends the working range of robots up to 5 m, allowing them to operate multiple workstations and perform a variety of tasks without manual repositioning. Compatible with over 60 cobots and small traditional robots.
Güdel Inc. is highlighting new technologies at Automate 2025 booth #2418 that demonstrate its unmatched ability to solve automation engineering challenges. One is the Cobomover, a 7th-axis linear track purpose-built for collaborative and lightweight robots. Designed and manufactured in Switzerland, this unit extends the working range of robots up to 5 m, allowing them to operate multiple workstations and perform a variety of tasks without manual repositioning. Compatible with over 60 cobots and small traditional robots.
Learn more and get all the specs.
New open-center XYZ stage
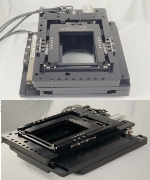 ThruSight-Focus is a high-performance, compact motion platform specifically engineered for applications requiring dual-side access to the sample or workpiece. It pairs ALIO's monolithic open-center XY stage -- known for its nanometer-level precision, crossed roller bearings, and direct linear drives -- with a novel Z-wedge mechanism that converts horizontal drive force into vertical motion via direct drive. This innovative architecture eliminates backlash, enhances servo responsiveness, and delivers fast, stable Z-axis movements -- all within a low-profile footprint.
ThruSight-Focus is a high-performance, compact motion platform specifically engineered for applications requiring dual-side access to the sample or workpiece. It pairs ALIO's monolithic open-center XY stage -- known for its nanometer-level precision, crossed roller bearings, and direct linear drives -- with a novel Z-wedge mechanism that converts horizontal drive force into vertical motion via direct drive. This innovative architecture eliminates backlash, enhances servo responsiveness, and delivers fast, stable Z-axis movements -- all within a low-profile footprint.
Learn more.
Eaton unveils differential engineered for EVs
 Intelligent power management company Eaton launched a new differential engineered specifically for electric vehicles at Auto Shanghai 2025 in China. The innovative design addresses the unique challenges presented by EV propulsion systems, including shared low-viscosity oil environments, increased sensitivity to noise, and the demands of high and instant torque delivery.
Intelligent power management company Eaton launched a new differential engineered specifically for electric vehicles at Auto Shanghai 2025 in China. The innovative design addresses the unique challenges presented by EV propulsion systems, including shared low-viscosity oil environments, increased sensitivity to noise, and the demands of high and instant torque delivery.
Read the full article.
Top Product: Integrated servo system is 20% smaller than standalone unit
 Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Read the full article.
Another success! NASA's Webb telescope reaches mirror alignment milestone

This artist's conception of the James Webb Space Telescope in space shows all its major elements fully deployed. The telescope was folded to fit into its launch vehicle, and then was slowly unfolded over the course of two weeks after launch. [Credits: NASA GSFC/CIL/Adriana Manrique Gutierre]
NASA's $10 billion, 7-ton James Webb Space Telescope, the world's largest and most complex space science telescope, has reached another milestone by completing critical alignment of its 18 hexagonal beryllium mirror segments.
Positioned nearly a million miles from Earth in its permanent orbit around the Sun, the telescope has had an incredible run of extremely difficult -- and flawless -- technical executions. These have included deploying its five-layer, tennis court-size sunshield and unfolding its 21-ft, gold-coated primary mirror made up of 18 segments.
The two wings of Webb's primary mirror had been folded to fit inside the nose cone of an Arianespace Ariane 5 rocket prior to launch on Dec. 25, 2021.
The Webb team began remotely unfolding the hexagonal segments of the primary mirror in the first week of January. This was a multi-day process, with the first side deployed Jan. 7 and the second Jan. 8.

For this stage of Webb's mirror alignment, known as "fine phasing," each of the primary mirror segments have been adjusted to produce one unified image of the same star (bottom image) using only the NIRCam instrument. This image of the star uses a red filter to optimize visual contrast. Top is the image of the 18 segments each focused on the same star prior to alignment (the same star shows up in 18 different locations). [Credits: NASA/STScI]
For the mirror alignment, the ground team commanded 126 actuators from Earth on the backsides of the segments to flex each mirror into precise position to within nanometers. On March 11, the Webb team completed the stage of alignment known as "fine phasing." At this key stage in the commissioning of
Webb's Optical Telescope Element, every optical parameter that has been checked and tested is performing at, or above, expectations. Now the 18 mirrors form a single mirror surface.
The team also found no critical issues and no measurable contamination or blockages to Webb's optical path. The observatory is able to successfully gather light from distant objects and deliver it to its instruments without issue.
While some of the largest ground-based telescopes on Earth use segmented primary mirrors, Webb is the first telescope in space to use such a design. The 21-ft, 4-in. primary mirror will now help Webb's primary imager, the Near-Infrared Camera, do its work.
Webb is designed to peer back over 13.5 billion years to capture infrared light from celestial objects, with much higher resolution than ever before, and to study our own solar system as well as distant worlds.
Although there are months to go before Webb ultimately delivers its new view of the cosmos, achieving this milestone means the team is confident that Webb's first-of-its-kind optical system is working as well as possible.

This new "selfie" was created using a specialized pupil imaging lens inside of the NIRCam instrument that was designed to take images of the primary mirror segments instead of images of the sky. This configuration is used strictly for engineering and alignment purposes. In this image, all of Webb's 18 primary mirror segments are shown collecting light from the same star in unison. [Credits: NASA/STScI]
Over the next six weeks, the team will proceed through the remaining alignment steps before final science instrument preparations. The team will further align the telescope to include the Near-Infrared Spectrograph, Mid-Infrared Instrument, and Near InfraRed Imager and Slitless Spectrograph. In this phase of the process, an algorithm will evaluate the performance of each instrument and then calculate the final corrections needed to achieve a well-aligned telescope across all science instruments. Following this, Webb's final alignment step will begin, and the team will adjust any small, residual positioning errors in the mirror segments.
The team is on track to conclude all aspects of Optical Telescope Element alignment by early May, if not sooner, before moving on to approximately two months of science instrument preparations. Webb's first full-resolution imagery and science data will be released in the summer.
Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners at ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.
Source: NASA
Published March 2022
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

