 |
| October 11, 2022 | Volume 18 Issue 38 |
Electrical/Electronic News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Test equipment advancing to meet rapidly changing market needs
 Although the rise of the IoT, 5G, and advanced automotive electronics markets is instigating rapid changes in technology, test equipment is keeping pace, and not just in extensions to bandwidth specifications or signal resolution. Maureen Lipps, Multicomp Pro Private Label Product Segment Leader, Test and Tools, Newark Electronics, runs through important advances in the industry and its tools.
Although the rise of the IoT, 5G, and advanced automotive electronics markets is instigating rapid changes in technology, test equipment is keeping pace, and not just in extensions to bandwidth specifications or signal resolution. Maureen Lipps, Multicomp Pro Private Label Product Segment Leader, Test and Tools, Newark Electronics, runs through important advances in the industry and its tools.
Read the full article.
Smallest rugged AI supercomputer for avionics
 Aitech Systems has released the A178-AV, the latest iteration of its smallest rugged GPGPU AI super-computers available with the powerful NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier System-on-Module. With its compact size, the A178-AV is the most advanced solution for artificial intelligence (AI), deep learning, and video and signal processing for next-gen avionic platforms.
Aitech Systems has released the A178-AV, the latest iteration of its smallest rugged GPGPU AI super-computers available with the powerful NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier System-on-Module. With its compact size, the A178-AV is the most advanced solution for artificial intelligence (AI), deep learning, and video and signal processing for next-gen avionic platforms.
Learn more.
Touchless angle sensors get CAN SAE J1939 interface
 Novotechnik has added the CAN J1939 interface (developed for heavy-duty vehicles) to its RFC4800 Series of touchless angle sensors measuring angular position up to 360°, turn direction, turns, speed, and operational status. It can provide one or two output channels. It has a longer life and robustness than an optical encoder. It can signal if a sensor needs replacing or average a programmable number of values to output to reduce external noise if present. This is wear-free angle measurement made easy.
Novotechnik has added the CAN J1939 interface (developed for heavy-duty vehicles) to its RFC4800 Series of touchless angle sensors measuring angular position up to 360°, turn direction, turns, speed, and operational status. It can provide one or two output channels. It has a longer life and robustness than an optical encoder. It can signal if a sensor needs replacing or average a programmable number of values to output to reduce external noise if present. This is wear-free angle measurement made easy.
Learn more.
Radar level sensor monitors liquids and powders
 The innovative FR Series non-contact radar level sensor from Keyence has been designed to monitor the level of both liquid and powder in any environment. This sensor features short- and long-range models, as well as chemical and sanitary options to address a wide array of level sensing applications. Works even when obstructions or harsh conditions are present, such as build-up, steam, or turbulence.
The innovative FR Series non-contact radar level sensor from Keyence has been designed to monitor the level of both liquid and powder in any environment. This sensor features short- and long-range models, as well as chemical and sanitary options to address a wide array of level sensing applications. Works even when obstructions or harsh conditions are present, such as build-up, steam, or turbulence.
Learn more.
Raspberry Pi launches $70 AI Kit
 Artificial intelligence (AI) is all the rage, and the makers of Raspberry Pi have created a way for enthusiasts of the single-board computer systems to take part and do a lot of experimenting along the way.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is all the rage, and the makers of Raspberry Pi have created a way for enthusiasts of the single-board computer systems to take part and do a lot of experimenting along the way.
Read the full article.
3D model sharing at Brother Industries cuts rework
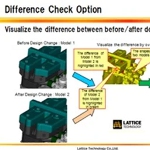 When Brother Industries, maker of printers, computers, and computer-related electronics, deployed Lattice Technology's XVL Player as a viewer for sharing 3D models throughout the processes of product design, parts design, mold design, mold production, and QA of molded parts, they reduced rework significantly -- especially from downstream departments. XVL Studio with its Difference Check Option helped address the rework in mold design, for example, by always keeping everyone informed of design changes.
When Brother Industries, maker of printers, computers, and computer-related electronics, deployed Lattice Technology's XVL Player as a viewer for sharing 3D models throughout the processes of product design, parts design, mold design, mold production, and QA of molded parts, they reduced rework significantly -- especially from downstream departments. XVL Studio with its Difference Check Option helped address the rework in mold design, for example, by always keeping everyone informed of design changes.
Read this real-world case study.
What is 3D-MID? Molded parts with integrated electronics from HARTING
 3D-MID (three-dimensional mechatronic integrated devices) technology combines electronic and mechanical functionalities into a single, 3D component. It replaces the traditional printed circuit board and opens up many new opportunities. It takes injection-molded parts and uses laser-direct structuring to etch areas of conductor structures, which are filled with a copper plating process to create very precise electronic circuits. HARTING, the technology's developer, says it's "Like a PCB, but 3D." Tons of possibilities.
3D-MID (three-dimensional mechatronic integrated devices) technology combines electronic and mechanical functionalities into a single, 3D component. It replaces the traditional printed circuit board and opens up many new opportunities. It takes injection-molded parts and uses laser-direct structuring to etch areas of conductor structures, which are filled with a copper plating process to create very precise electronic circuits. HARTING, the technology's developer, says it's "Like a PCB, but 3D." Tons of possibilities.
Learn more (video included on page).
New! Thermoelectric dehumidifiers for enclosures
 Seifert Systems has just introduced its line of compact Soliflex® Series thermoelectric dehumidifiers, with or without condensate pump. These IP 56-rated units are designed to dehumidify enclosures and small control panels, can be used indoors or outdoors, and are maintenance free. When used with a hygrostat, Soliflex dehumidifiers will keep enclosure humidity below a defined level and only operate when needed.
Seifert Systems has just introduced its line of compact Soliflex® Series thermoelectric dehumidifiers, with or without condensate pump. These IP 56-rated units are designed to dehumidify enclosures and small control panels, can be used indoors or outdoors, and are maintenance free. When used with a hygrostat, Soliflex dehumidifiers will keep enclosure humidity below a defined level and only operate when needed.
Learn more.
More Stego enclosure heater options from AutomationDirect
 Automation-Direct has added more Stego enclosure heaters to their Enclosure Thermal Management lineup. These new 120 to 240 VAC/VDC units include small, flat versions that distribute heat evenly within compact enclosures and are available with 8- or 10-W heating capacities. Also added are compact loop heaters that feature a patented loop body design for increased natural convection airflow, reduced thermal stress on the heater, and better heat transfer. Loop heaters are available in 10- to 150-W heating capacities.
Automation-Direct has added more Stego enclosure heaters to their Enclosure Thermal Management lineup. These new 120 to 240 VAC/VDC units include small, flat versions that distribute heat evenly within compact enclosures and are available with 8- or 10-W heating capacities. Also added are compact loop heaters that feature a patented loop body design for increased natural convection airflow, reduced thermal stress on the heater, and better heat transfer. Loop heaters are available in 10- to 150-W heating capacities.
Learn more.
Great design: Handle with integrated lighting/signaling
 Signaling and indicator lights, switches, and buttons -- elements that hardly any machine can do without. The new JW Winco cabinet U-handle EN 6284 integrates all these functions into a single, compact element. The new U-handle is designed to enhance the operation of systems and machines. It features an integrated button and a large, colored, backlit area on the back of the handle. These elements can be used individually or in combination, providing a versatile tool for system control and process monitoring that can be seen from across the room.
Signaling and indicator lights, switches, and buttons -- elements that hardly any machine can do without. The new JW Winco cabinet U-handle EN 6284 integrates all these functions into a single, compact element. The new U-handle is designed to enhance the operation of systems and machines. It features an integrated button and a large, colored, backlit area on the back of the handle. These elements can be used individually or in combination, providing a versatile tool for system control and process monitoring that can be seen from across the room.
Learn more.
Engineer's Toolbox: What is ground loop feedback?
 Improper grounding can create problems in data logging, data acquisition, and measurement and control systems. One of the most common problems is known as ground loop feedback. Experts at CAS DataLoggers run through five ways to eliminate this problem.
Improper grounding can create problems in data logging, data acquisition, and measurement and control systems. One of the most common problems is known as ground loop feedback. Experts at CAS DataLoggers run through five ways to eliminate this problem.
Read the full article.
AI development kit for multi-camera products
 The QCS6490 Vision-AI Development Kit from Avnet enables engineering teams to rapidly prototype hardware, application software, and AI enablement for multi-camera, high-performance, Edge AI-enabled custom embedded products. The kit facilitates design with the new, energy-efficient MSC SM2S-QCS6490 SMARC compute module based on the Qualcomm QCS6490 processor. Provides support for up to four MIPI CSI cameras and concurrent Mini DisplayPort and MIPI DSI displays.
The QCS6490 Vision-AI Development Kit from Avnet enables engineering teams to rapidly prototype hardware, application software, and AI enablement for multi-camera, high-performance, Edge AI-enabled custom embedded products. The kit facilitates design with the new, energy-efficient MSC SM2S-QCS6490 SMARC compute module based on the Qualcomm QCS6490 processor. Provides support for up to four MIPI CSI cameras and concurrent Mini DisplayPort and MIPI DSI displays.
Learn more.
High-temp cabinet cooler keeps incineration process in business
 An EXAIR client company handles waste treatment on a large ship by operating an incinerator. The area where the incinerator is located gets very hot (over 120° F). This causes failures in the electronics package used to control the incineration process. Since compressed air is readily available, EXAIR's Model HT4225 Cabinet Cooler System is being used to keep the panel cool. It saved the customer from having to replace their control units due to the hot conditions in the incinerator room. Thermostat control is also available, conserving air and operating only when needed to minimize air consumption.
An EXAIR client company handles waste treatment on a large ship by operating an incinerator. The area where the incinerator is located gets very hot (over 120° F). This causes failures in the electronics package used to control the incineration process. Since compressed air is readily available, EXAIR's Model HT4225 Cabinet Cooler System is being used to keep the panel cool. It saved the customer from having to replace their control units due to the hot conditions in the incinerator room. Thermostat control is also available, conserving air and operating only when needed to minimize air consumption.
Learn about EXAIR's huge selection of Cabinet Coolers.
Compact snap-in capacitors for general-purpose applications
 TDK's new EPCOS B43659 series of snap-in aluminum electrolytic capacitors is the next generation of ultra-compact, general-purpose components for voltages of 450 V (DC) featuring an extremely high CV product. It provides the same features and serves the same applications as the previous series but is much more compact. These RoHS-compliant capacitors can be used in a wide range of applications, such as switched-mode power supplies, frequency converters, UPS, medical equipment, and solar inverters.
TDK's new EPCOS B43659 series of snap-in aluminum electrolytic capacitors is the next generation of ultra-compact, general-purpose components for voltages of 450 V (DC) featuring an extremely high CV product. It provides the same features and serves the same applications as the previous series but is much more compact. These RoHS-compliant capacitors can be used in a wide range of applications, such as switched-mode power supplies, frequency converters, UPS, medical equipment, and solar inverters.
Get all the specs.
Conductive Brush Ring overcomes current leakage in EV powertrains
 SKF's new Conductive Brush Ring paves the way to greater reliability and longer life in high-performance electric vehicle powertrain systems. Using pure carbon fiber bristles, it provides a reliable electrical connection between an EV eAxle rotor shaft and its housing. When used in combination with SKF Hybrid ceramic ball bearings, it helps to alleviate parasitic current effects that can lead to premature failure in bearings and other components. Available in different configurations for wet (oil-lubricated) motor designs -- and soon for dry (sealed) applications.
SKF's new Conductive Brush Ring paves the way to greater reliability and longer life in high-performance electric vehicle powertrain systems. Using pure carbon fiber bristles, it provides a reliable electrical connection between an EV eAxle rotor shaft and its housing. When used in combination with SKF Hybrid ceramic ball bearings, it helps to alleviate parasitic current effects that can lead to premature failure in bearings and other components. Available in different configurations for wet (oil-lubricated) motor designs -- and soon for dry (sealed) applications.
Learn more.
Researchers use infrared light to wirelessly transmit power over 30 meters

A new system uses infrared light to safely transfer power over distances up to 30 m. This type of long-range optical wireless power transfer system could enable real-time power transmission to fixed and mobile receivers. [Credit: Jinyong Ha, Sejong University]
Imagine walking into an airport or grocery store and your smartphone automatically starts charging. This could be a reality one day, thanks to a new wireless laser charging system that overcomes some of the challenges that have hindered previous attempts to develop safe and convenient, on-the-go charging systems.
"The ability to power devices wirelessly could eliminate the need to carry around power cables for our phones or tablets," said research team leader Jinyong Ha from Sejong University in South Korea. "It could also power various sensors such as those in Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors used for monitoring processes in manufacturing plants."
In the Optica Publishing Group journal Optics Express, the researchers describe their new system, which uses infrared light to safely transfer high levels of power. Laboratory tests showed that it could transfer 400-mW light power over distances up to 30 m. This power is sufficient for charging sensors and, with further development, it could be increased to levels necessary to charge mobile devices.
Several techniques have been studied for long-range wireless power transfer. However, it has been difficult to safely send enough power over meter-level distances. To overcome this challenge, the researchers optimized a method called distributed laser charging, which has recently gained more attention for this application because it provides safe, high-power illumination with less light loss.
"While most other approaches require the receiving device to be in a special charging cradle or to be stationary, distributed laser charging enables self-alignment without tracking processes as long as the transmitter and receiver are in the line of sight of each other," said Ha. "It also automatically shifts to a safe, low-power delivery mode if an object or a person blocks the line of sight."
Going the distance
Distributed laser charging works somewhat like a traditional laser, but instead of the optical components of the laser cavity being integrated into one device, they are separated into a transmitter and receiver. When the transmitter and receiver are within a line of sight, a laser cavity is formed between them over the air (or free space), which allows the system to deliver light-based power. If an obstacle cuts the transmitter-receiver line of sight, the system automatically switches to a power-safe mode, achieving hazard-free power delivery in the air.
In the new system, the researchers used an erbium-doped fiber amplifier optical power source with a central wavelength of 1,550 nm. This wavelength range is in the safest region of the spectrum and poses no danger to human eyes or skin at the power used. Another key component was a wavelength division multiplexing filter that created a narrowband beam with optical power within the safety limits for free space propagation.
"In the receiver unit, we incorporated a spherical ball lens retroreflector to facilitate 360-degree transmitter-receiver alignment, which maximized the power transfer efficiency," said Ha. "We experimentally observed that the system's overall performance depended on the refractive index of the ball lens, with a 2.003 refractive index being the most effective."
Lab testing
To demonstrate the system, the researchers set up a 30-m separation between a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter was made of the erbium-doped fiber amplifier optical source, and the receiver unit included a retroreflector, a photovoltaic cell that converts the optical signal to electrical power and an LED that illuminates when power is being delivered. This receiver, which is about 10 x 10 mm, could easily be integrated into devices and sensors.

The new system includes a transmitter that consists of an erbium-doped fiber amplifier optical power source and a receiver with a ball lens retroreflector that helps boost performance. [Credit: Jinyong Ha, Sejong University]
The experimental results showed that a single-channel wireless optical power transfer system could provide an optical power of 400 mW with a channel linewidth of 1 nm over a distance of 30 m. The photovoltaic converted this to an electrical power of 85 mW. The researchers also showed that the system automatically shifted to a safe power transfer mode when the line of sight was interrupted by a human hand. In this mode, the transmitter produced an incredibly low-intensity light that did not pose any risk to people.
"Using the laser charging system to replace power cords in factories could save on maintenance and replacement costs," said Ha. "This could be particularly useful in harsh environments where electrical connections can cause interference or pose a fire hazard."
Now that they have demonstrated the system, the researchers are working to make it more practical. For example, the efficiency of the photovoltaic cell could be increased to better convert light into electrical power. They also plan to develop a way to use the system to charge multiple receivers simultaneously.
Source: Optics Express
Published October 2022
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
