 |
| November 12, 2024 | Volume 20 Issue 43 |
Electrical/Electronic News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Isolated probing tech for fast-switching power device testing
 Keysight Technologies has developed an optically isolated differential probing family dedicated to enhancing efficiency and performance testing of fast-switching devices such as wide-bandgap GaN and SiC semiconductors. Validation of floating half-bridge and full-bridge architectures commonly used in power conversion, motor drives, and inverters requires measurement of small differential signals riding on high common-mode voltages. This measurement can be challenging due to voltage source fluctuations relative to ground, noise interference, and safety concerns.
Keysight Technologies has developed an optically isolated differential probing family dedicated to enhancing efficiency and performance testing of fast-switching devices such as wide-bandgap GaN and SiC semiconductors. Validation of floating half-bridge and full-bridge architectures commonly used in power conversion, motor drives, and inverters requires measurement of small differential signals riding on high common-mode voltages. This measurement can be challenging due to voltage source fluctuations relative to ground, noise interference, and safety concerns.
Learn more.
Protect sensitive electronics in explosive environments with new aluminum ATEX Cabinet Cooler Systems
 EXAIR's ATEX Cabinet Cooler® Systems deliver a powerful and affordable solution for keeping electrical enclosures cool in hazardous ATEX classified areas -- and they're now available in durable aluminum construction. Engineered for use in Zones 2 and 22, these coolers are UL tested, CE compliant, and meet stringent ATEX standards for purged and pressurized enclosures. With cooling capacities up to 5,600 Btu/Hr., ATEX Cabinet Coolers are ideal for preventing overheating in electrical cabinets. EXAIR offers a comprehensive lineup of systems.
EXAIR's ATEX Cabinet Cooler® Systems deliver a powerful and affordable solution for keeping electrical enclosures cool in hazardous ATEX classified areas -- and they're now available in durable aluminum construction. Engineered for use in Zones 2 and 22, these coolers are UL tested, CE compliant, and meet stringent ATEX standards for purged and pressurized enclosures. With cooling capacities up to 5,600 Btu/Hr., ATEX Cabinet Coolers are ideal for preventing overheating in electrical cabinets. EXAIR offers a comprehensive lineup of systems.
Learn more.
PLC handbook chock full of must-know information
 Automation-Direct's Practical Guide to Program-mable Logic Controllers Handbook has been improved with tons of new need-to-know info, making it a more comprehensive guide to the world of PLCs. Besides covering the basics of PLC history, PLC hardware, and PLC software, this guide takes you deeper into the ever-changing world of PLC communication, the importance of feedback loops, cyber security, and many other areas that are a must-know for any PLC novice or seasoned automation professional.
Automation-Direct's Practical Guide to Program-mable Logic Controllers Handbook has been improved with tons of new need-to-know info, making it a more comprehensive guide to the world of PLCs. Besides covering the basics of PLC history, PLC hardware, and PLC software, this guide takes you deeper into the ever-changing world of PLC communication, the importance of feedback loops, cyber security, and many other areas that are a must-know for any PLC novice or seasoned automation professional.
Get this great resource today.
Haptic feedback prototyping kit from TDK
 Get your customers to feel the difference your products make. TDK has released a development starter kit for fast haptics prototyping. It gives mechanical designers and engineers first impressions of the haptic feedback using PowerHap piezo actuators, shows how the mechanical integration works, and provides a reference design. Applications include automotive, displays and tablets, household appliances, vending machines, game controllers, industrial equipment, and medical devices.
Get your customers to feel the difference your products make. TDK has released a development starter kit for fast haptics prototyping. It gives mechanical designers and engineers first impressions of the haptic feedback using PowerHap piezo actuators, shows how the mechanical integration works, and provides a reference design. Applications include automotive, displays and tablets, household appliances, vending machines, game controllers, industrial equipment, and medical devices.
Learn more.
Mini ESD preset torque screwdriver
 Need precision fastening with ESD protection at the smallest torque levels? Mountz has you covered. The new FG Mini ESD Preset Torque Screwdriver is built for low-torque, high-precision tasks. Its compact design makes it ideal for tight spaces and small fasteners, while delivering the same reliable control and ESD protection users have come to expect from Mountz. Two models available: FG25z (3 to 25 ozf.in, 2 to 17.7 cN-m) and FG50z (20 to 50 ozf.in, 14.1 to 35.3 cN-m).
Need precision fastening with ESD protection at the smallest torque levels? Mountz has you covered. The new FG Mini ESD Preset Torque Screwdriver is built for low-torque, high-precision tasks. Its compact design makes it ideal for tight spaces and small fasteners, while delivering the same reliable control and ESD protection users have come to expect from Mountz. Two models available: FG25z (3 to 25 ozf.in, 2 to 17.7 cN-m) and FG50z (20 to 50 ozf.in, 14.1 to 35.3 cN-m).
Learn more.
Laumas load cells and electronics from AutomationDirect
 Automation-Direct has added Laumas precision-engineered load cells, transmitters, and accessories that deliver reliable performance in industrial weighing and force measurement applications. The FCAL series high-precision bending beam load cells are ideal for low- to mid-capacity systems. CTL series load cells are designed for both tension and compression, with excellent linearity. The CBL series low-profile compression load cells are perfect for space-limited applications. Laumas load cell transmitters are available too for precise monitoring and control. Very good pricing.
Automation-Direct has added Laumas precision-engineered load cells, transmitters, and accessories that deliver reliable performance in industrial weighing and force measurement applications. The FCAL series high-precision bending beam load cells are ideal for low- to mid-capacity systems. CTL series load cells are designed for both tension and compression, with excellent linearity. The CBL series low-profile compression load cells are perfect for space-limited applications. Laumas load cell transmitters are available too for precise monitoring and control. Very good pricing.
Learn more.
Engineer's Toolbox: What is ground loop feedback?
 Improper grounding can create problems in data logging, data acquisition, and measurement and control systems. One of the most common problems is known as ground loop feedback. Experts at CAS DataLoggers run through five ways to eliminate this problem.
Improper grounding can create problems in data logging, data acquisition, and measurement and control systems. One of the most common problems is known as ground loop feedback. Experts at CAS DataLoggers run through five ways to eliminate this problem.
Read the full article.
What is a braking resistor?
 According to Automation-Direct, "Braking resistors don't actually provide braking directly -- rather, they allow a drive to stop a loaded motor faster." Why is this important? Protect your AC or DC drive system from regenerative voltage that can create an over-voltage fault on the drive -- especially with high inertial loads or rapid deceleration.
According to Automation-Direct, "Braking resistors don't actually provide braking directly -- rather, they allow a drive to stop a loaded motor faster." Why is this important? Protect your AC or DC drive system from regenerative voltage that can create an over-voltage fault on the drive -- especially with high inertial loads or rapid deceleration.
View the video.
New Digital Static Meter: Precise measurement, easy use
 Static electricity isn't just a nuisance; it's a serious threat to manufacturing efficiency, product integrity, and workplace safety. Unchecked static can lead to costly downtime, product defects, material jams, and even hazardous shocks to employees. If static is interfering with your processes, EXAIR's upgraded Model 7905 Digital Static Meter offers an essential first step in identifying and eliminating the problem. With just the press of a button, this easy-to-use, handheld device pinpoints the highest voltage areas in your facility, helping you diagnose static issues before they become a problem.
Static electricity isn't just a nuisance; it's a serious threat to manufacturing efficiency, product integrity, and workplace safety. Unchecked static can lead to costly downtime, product defects, material jams, and even hazardous shocks to employees. If static is interfering with your processes, EXAIR's upgraded Model 7905 Digital Static Meter offers an essential first step in identifying and eliminating the problem. With just the press of a button, this easy-to-use, handheld device pinpoints the highest voltage areas in your facility, helping you diagnose static issues before they become a problem.
Learn more.
New laser cutting modulating strategy tested with Mikrotron high-speed camera
 Modulating a laser beam's intensity distribution optimizes energy delivery to the process zone, resulting in better cutting speed, cut edge quality, and cut kerf geometry. Scientists in Belgium have come up with a new method that they say produces better cutting results.
Modulating a laser beam's intensity distribution optimizes energy delivery to the process zone, resulting in better cutting speed, cut edge quality, and cut kerf geometry. Scientists in Belgium have come up with a new method that they say produces better cutting results.
Read the full article.
All-in-one embedded PLC based on Raspberry Pi 4 -- build control applications
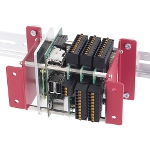 The new PLC CPI-PS10CM4 from Contec Co. is a compact embedded programmable logic controller (PLC) that is loaded with CODESYS, the world's most widely used software PLC. This product uses Contec's original single-board computer, which is based on Raspberry Pi's latest embedded module, the Compute Module 4 (CM4). By using the wide range of peripheral devices for Raspberry Pi, such as Contec's CPI Series, you can build various control applications in a PLC language that complies with the IEC 61131-3 international standard.
The new PLC CPI-PS10CM4 from Contec Co. is a compact embedded programmable logic controller (PLC) that is loaded with CODESYS, the world's most widely used software PLC. This product uses Contec's original single-board computer, which is based on Raspberry Pi's latest embedded module, the Compute Module 4 (CM4). By using the wide range of peripheral devices for Raspberry Pi, such as Contec's CPI Series, you can build various control applications in a PLC language that complies with the IEC 61131-3 international standard.
Learn more.
Torque sensors for fastening applications and more
 Saelig Company has introduced the Sensor Technology SGR525/526 Series Torque Sensors to provide precision torque monitoring that is critical for performance and safety. The square drive design (for applications with non-cylindrical shafts) allows for seamless integration into power tools, test rigs, industrial machinery, and precision fastening applications, ensuring superior torque measurement without the need for additional adapters or modifications. The SGR525 offers torque measurement only, while the SGR526 provides torque, speed, and power measurement using a 360-pulse-per-revolution encoder. Industries include automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and research and development.
Saelig Company has introduced the Sensor Technology SGR525/526 Series Torque Sensors to provide precision torque monitoring that is critical for performance and safety. The square drive design (for applications with non-cylindrical shafts) allows for seamless integration into power tools, test rigs, industrial machinery, and precision fastening applications, ensuring superior torque measurement without the need for additional adapters or modifications. The SGR525 offers torque measurement only, while the SGR526 provides torque, speed, and power measurement using a 360-pulse-per-revolution encoder. Industries include automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and research and development.
Learn more.
Wide-angle camera optimized for larger, faster conveyor belts
 Wider conveyor belts operating at higher speeds are now commonplace in modern logistics. To keep up, SVS-Vistek is offering a cost-effective alternative to multi-camera systems with its fxo901CXGE 10-GigE color camera featuring the Sony IMX901-AQR wide-aspect global shutter 16.4-megapixel CMOS sensor. Unlike standard cameras, this unit captures targets in a wide field of view while maintaining high resolutions. The 4:1 horizontal aspect ratio allows one fxo901CXGE to replace an entire multi-camera system, removing the need for image synchronization.
Wider conveyor belts operating at higher speeds are now commonplace in modern logistics. To keep up, SVS-Vistek is offering a cost-effective alternative to multi-camera systems with its fxo901CXGE 10-GigE color camera featuring the Sony IMX901-AQR wide-aspect global shutter 16.4-megapixel CMOS sensor. Unlike standard cameras, this unit captures targets in a wide field of view while maintaining high resolutions. The 4:1 horizontal aspect ratio allows one fxo901CXGE to replace an entire multi-camera system, removing the need for image synchronization.
Learn more.
Handheld thermal imager cuts diagnostic time
 The FLIR TG268 is a next-generation thermal imager that provides professionals in the utility, manufacturing, electrical, automotive, and industrial sectors with a lightweight, handheld, affordable condition monitoring tool. Latest enhancements include higher temperature ranges, improved resolution, and larger data storage capacity. Go beyond the restrictions of single-spot IR thermometers to view and evaluate hot and cold spots that may signify potentially dangerous issues. Accurately measure temps from -25 to 400 C. Native thermal images improved with Super Resolution upscaling.
The FLIR TG268 is a next-generation thermal imager that provides professionals in the utility, manufacturing, electrical, automotive, and industrial sectors with a lightweight, handheld, affordable condition monitoring tool. Latest enhancements include higher temperature ranges, improved resolution, and larger data storage capacity. Go beyond the restrictions of single-spot IR thermometers to view and evaluate hot and cold spots that may signify potentially dangerous issues. Accurately measure temps from -25 to 400 C. Native thermal images improved with Super Resolution upscaling.
Learn more.
SOLIDWORKS 2025: Sheet metal design top features from an expert
 Find out what's new in SOLIDWORKS 2025 when it comes to sheet metal and weldments, and learn some valuable tips and tricks along the way from TriMech. Topics covered include copying cut list properties, bend notches, tab and slot enhancements, groove beads (a new type of weld bead), performance enhancements, and more. When you're done, check out TriMech's full YouTube channel filled with educational material.
Find out what's new in SOLIDWORKS 2025 when it comes to sheet metal and weldments, and learn some valuable tips and tricks along the way from TriMech. Topics covered include copying cut list properties, bend notches, tab and slot enhancements, groove beads (a new type of weld bead), performance enhancements, and more. When you're done, check out TriMech's full YouTube channel filled with educational material.
View the video.
It may have impressive output, but generative AI doesn't have a coherent understanding of the world
Researchers show that even the best-performing large language models don't form a true model of the world and its rules -- and can thus fail unexpectedly on similar tasks.
By Adam Zewe, MIT
Large language models (LLMs) can do impressive things, like write poetry or generate viable computer programs, even though these models are trained to predict words that come next in a piece of text. Such surprising capabilities can make it seem like the models are implicitly learning some general truths about the world.
That isn't necessarily the case, according to a new study. The researchers found that a popular type of generative artificial intelligence (AI) model can provide turn-by-turn driving directions in New York City with near-perfect accuracy -- without having formed an accurate internal map of the city.
Despite the model's uncanny ability to navigate effectively, when the researchers closed some streets and added detours, its performance plummeted. When they dug deeper, the researchers found that the New York maps the model implicitly generated had many nonexistent streets curving between the grid and connecting far-away intersections.
This could have serious implications for generative AI models deployed in the real world, since a model that seems to be performing well in one context might break down if the task or environment slightly changes.
"One hope is that, because LLMs can accomplish all these amazing things in language, maybe we could use these same tools in other parts of science, as well. But the question of whether LLMs are learning coherent world models is very important if we want to use these techniques to make new discoveries," says senior author Ashesh Rambachan, assistant professor of economics and a principal investigator in the MIT Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems (LIDS).
Rambachan is joined on a paper about the work by lead author Keyon Vafa, a postdoc at Harvard University; Justin Y. Chen, an electrical engineering and computer science (EECS) graduate student at MIT; Jon Kleinberg, Tisch University Professor of Computer Science and Information Science at Cornell University; and Sendhil Mullainathan, an MIT professor in the departments of EECS and of Economics, and a member of LIDS. The research will be presented at the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems in December 2024.
New metrics
The researchers focused on a type of generative AI model known as a transformer, which forms the backbone of LLMs like GPT-4. Transformers are trained on a massive amount of language-based data to predict the next token in a sequence, such as the next word in a sentence.
However, if scientists want to determine whether an LLM has formed an accurate model of the world, measuring the accuracy of its predictions doesn't go far enough, the researchers say. For example, they found that a transformer can predict valid moves in a game of Connect 4 nearly every time without understanding any of the rules. So, the team developed two new metrics that can test a transformer's world model. The researchers focused their evaluations on a class of problems called deterministic finite automations, or DFAs.
A DFA is a problem with a sequence of states, like intersections one must traverse to reach a destination, and a concrete way of describing the rules one must follow along the way. They chose two problems to formulate as DFAs: navigating on streets in New York City and playing the board game Othello.
"We needed test beds where we know what the world model is. Now, we can rigorously think about what it means to recover that world model," Vafa explains.
The first metric they developed, called sequence distinction, says a model has formed a coherent world model it if sees two different states, like two different Othello boards, and recognizes how they are different. Sequences, that is, ordered lists of data points, are what transformers use to generate outputs.
The second metric, called sequence compression, says a transformer with a coherent world model should know that two identical states, like two identical Othello boards, have the same sequence of possible next steps.
They used these metrics to test two common classes of transformers, one which is trained on data generated from randomly produced sequences and the other on data generated by following strategies.
Incoherent world models
Surprisingly, the researchers found that transformers that made choices randomly formed more accurate world models, perhaps because they saw a wider variety of potential next steps during training.
"In Othello, if you see two random computers playing rather than championship players, in theory you'd see the full set of possible moves, even the bad moves championship players wouldn't make," Vafa explains.
Even though the transformers generated accurate directions and valid Othello moves in nearly every instance, the two metrics revealed that only one generated a coherent world model for Othello moves, and none performed well at forming coherent world models in the wayfinding example.
The researchers demonstrated the implications of this by adding detours to the map of New York City, which caused all the navigation models to fail.
"I was surprised by how quickly the performance deteriorated as soon as we added a detour. If we close just 1 percent of the possible streets, accuracy immediately plummets from nearly 100 percent to just 67 percent," Vafa says.
When they recovered the city maps the models generated, they looked like an imagined New York City with hundreds of streets crisscrossing overlaid on top of the grid. The maps often contained random flyovers above other streets or multiple streets with impossible orientations.
These results show that transformers can perform surprisingly well at certain tasks without understanding the rules. If scientists want to build LLMs that can capture accurate world models, they need to take a different approach, the researchers say.
"Often, we see these models do impressive things and think they must have understood something about the world. I hope we can convince people that this is a question to think very carefully about, and we don't have to rely on our own intuitions to answer it," says Rambachan.
In the future, the researchers want to tackle a more diverse set of problems, such as those where some rules are only partially known. They also want to apply their evaluation metrics to real-world, scientific problems.
Published November 2024
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
