 |
| January 06, 2015 | Volume 11 Issue 01 |
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Army engineers developing safer, more accurate tracer round
The goal is a to develop a tracer that will give only those at the shooter location the ability to see where the round is headed.
By Audra Calloway, Picatinny Arsenal, NJ
Engineers at the U.S. Army's Picatinny Arsenal are researching a way to develop a new type of tracer round that not only would perform its function during the day as well as night, but also improve shooter accuracy and keep Soldiers safer by reducing their visual signature.

Tracer rounds ricochet off of a tank as security police fire a mounted .50-caliber machine gun. [Photo Credit: Staff Sgt. Angela Stafford]
Tracer rounds, which are usually loaded as every fifth round in machine gun belts, provide essential information to Soldiers firing at an enemy target by creating a line of sight that allows them to track the trajectory of their bullets and adjust their aim.
However, the pyrotechnic streak they emit also gives away the shooter's location by allowing the enemy to follow the line of the pyrotechnic trail back to the shooter.

Tracer rounds ricochet off of a tank as security police fire a mounted .50-caliber machine gun. [Photo Credit: Staff Sgt. Angela Stafford]
The One-Way Luminescence, or OWL, tracer round being developed by engineers at the Armament Research, Development and Engineering Center, known as ARDEC, will give only those at the shooter location the ability to see where the round is headed without revealing their position. This will keep Soldiers safer because their location will not be observable to the enemy.
Current tracer projectiles have a longer jacket, in comparison to their ball projectile counterparts, in order to incorporate a cavity that is packed with pyrotechnics. As the bullet flies through the air, the pyrotechnics burn and emit a flame that can be seen from all angles from the back of the round, which allows the enemy to see the shooter's position.

The photo shows the differences in shape and size between the 7.62mm legacy tracer, legacy M80 ball, and M80A1 rounds. [Photo Credit: U.S. Army photo]

A cut-away view of the current tracer round, which burns pyrotechnics to produce a streak of light. [Photo Credit: U.S. Army photo]
"OWL is a technology approach that doesn't allow an enemy target to trace back to who is firing rounds at him, even if the target is using night vision goggles," said Christel Seitel, Quality Assurance Lead for the OWL program.
Development challenges
ARDEC engineers are experimenting with a variety of potential solutions. With one of the OWL technology concepts, "We're just putting a thin layer of material on the back [only] of the ball round. So, instead of burning pyrotechnics, our luminescence is like a glow-in-the-dark sticker. You excite it with specific wavelengths of light," says Seitel.
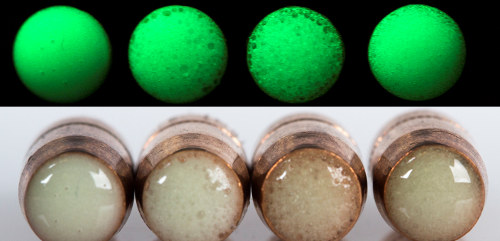
Potential One Way Luminescence concepts, activated (top) and inactive. [Photo Credit: U.S. Army graphic]
"The ultimate goal is to replace the tracer rounds with the OWL rounds and, potentially, put OWL on the back of every ball round," Seitel says.
A ball round is a standard, general-purpose round, which was developed to be lethal. ARDEC scientists are currently exploring options to achieve this, looking at different coatings and materials to find a solution that satisfies the Army's requirement to be both a day and night tracer.
"Finding something that burns brighter than the sun is difficult," Seitel says of the technology development goal. "You want to have something that's bright enough to give you that contrast [with the background]."
Because little to no material is ejected from an OWL projectile, finding a technology that meets or exceeds the light output of a current pyrotechnic tracer is extremely challenging.
"Because we don't completely know what path we're taking, we're looking at all our options, and we will hopefully down-select in a few years," Seitel says.
In addition to the in-house design effort, multiple contracts have been awarded in fiscal year 2014 using the Defense Ordnance Technology Consortium process to seek competitive prototype designs from industry.
Striving for heightened accuracy
A final OWL design is anticipated to be down-selected in fiscal year 2017, and transition to an Engineering and Manufacturing Development program at that time. Current pyrotechnic tracer rounds lose mass as the pyrotechnics burn, so they don't completely mimic the trajectory of the ball rounds, which don't lose mass.
Since it is anticipated that OWL will be applied to all ball rounds, effectively making ball rounds trace without the need of a cavity, they will all have the same trajectory. And since the shooter can see the exact trajectory of where his round is heading, he can quickly make adjustments to get on target faster.
Safer to manufacture
The OWL also has the potential for safer manufacturing.
Because many of the OWL concepts will not contain pyrotechnic material, it will also be safer and less sensitive to handle in a production environment. However, there are a few OWL concepts that contain limited amounts of energetic material to try and overcome the sun's light output.
"Currently, the pyrotechnics have a separate wing in manufacturing plants due to safety concerns. But if you can just make your bullets and then paste something on the back, you won't have the costs of special handling," says Seitel.
OWL is a joint effort by ARDEC, the Program Executive Office for Ammunition, the Joint Service Small Arms Program Office, Army Corps of Engineers, Army Research Laboratory, Naval Research Laboratory and Night Vision Laboratory.
PM-MAS, which is also part of the joint effort, has supported ARDEC in obtaining science and technology funding, and plans to transition OWL to a formal acquisition program in fiscal year 2015.
The Armament Research, Development and Engineering Center is part of the U.S. Army Research, Development and Engineering Command, which has the mission to develop technology and engineering solutions for America's Soldiers.
Published August 2014
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
