 |
| June 09, 2015 | Volume 11 Issue 22 |
Motion Control News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Versatile Transport System: Turbocharge conveyance
 THK's Versatile Transport System is a high-mix production solution that will keep your production line moving. Its linear motor drive enables high-speed operations, and processing can be performed directly on top of the system's freely recirculating sliders. This highly precise, modular system has many unique features, including easily adjustable stop positions, flex layouts with path splitting and parallelization, and easy addition/subtraction of extension pieces.
THK's Versatile Transport System is a high-mix production solution that will keep your production line moving. Its linear motor drive enables high-speed operations, and processing can be performed directly on top of the system's freely recirculating sliders. This highly precise, modular system has many unique features, including easily adjustable stop positions, flex layouts with path splitting and parallelization, and easy addition/subtraction of extension pieces.
View the video.
Tech Tip: How to keep heavy loads balanced
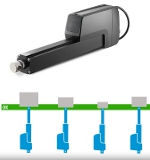 Some Thomson smart linear actuators have a position-based synchro-nization option to help manage unbalanced loads when using multiple units. The system adjusts the speed of each actuator to keep them starting, moving, and stopping synchronously, regardless of their respective load distribution. So useful. So smart.
Some Thomson smart linear actuators have a position-based synchro-nization option to help manage unbalanced loads when using multiple units. The system adjusts the speed of each actuator to keep them starting, moving, and stopping synchronously, regardless of their respective load distribution. So useful. So smart.
Learn all about this feature.
Micropositioning stages ensure high accuracy
 PI now offers fast delivery of the L-511 linear microposi-tioning stage, which is designed for applications requiring minimum incremental motion down to 20 nm and drive forces up to 22 lb. The L-511 can be combined to form XY or XYZ motion systems and integrated with rotary stages for enhanced flexibility. Features high-load recirculating ball bearings for exceptional durability, even under demanding, repetitive cycles. To enhance positioning accuracy and automation throughput, this stage integrates non-contact, direction-sensing optical reference point switches located at mid-travel.
PI now offers fast delivery of the L-511 linear microposi-tioning stage, which is designed for applications requiring minimum incremental motion down to 20 nm and drive forces up to 22 lb. The L-511 can be combined to form XY or XYZ motion systems and integrated with rotary stages for enhanced flexibility. Features high-load recirculating ball bearings for exceptional durability, even under demanding, repetitive cycles. To enhance positioning accuracy and automation throughput, this stage integrates non-contact, direction-sensing optical reference point switches located at mid-travel.
Learn more.
Robots think and act on the fly at moving assembly line speeds
 Inbolt and FANUC are launching a manufacturing breakthrough enabling FANUC robots to tackle one of the most complex automation challenges: performing production tasks on continuously moving parts at line speeds. With Inbolt's AI-powered 3D vision, manufacturers can now automate screw insertion, bolt rundown, glue application, and other high-precision tasks on parts moving down the line without costly infrastructure investments or cycle time compromises.
Inbolt and FANUC are launching a manufacturing breakthrough enabling FANUC robots to tackle one of the most complex automation challenges: performing production tasks on continuously moving parts at line speeds. With Inbolt's AI-powered 3D vision, manufacturers can now automate screw insertion, bolt rundown, glue application, and other high-precision tasks on parts moving down the line without costly infrastructure investments or cycle time compromises.
Learn more.
Best high-speed rotary bearing in THK history
 THK has developed its best-performing, high-speed rotary bearing ever: the High-Speed, Double-Row Angular Contact Ring BWH. This rotary bearing has balls aligned inside a cage between the inner and outer rings and is part of the THK Rotary Series, along with the cross-roller ring. The main features of this product are its ability to receive loads in all directions as well as its high rigidity and rotational accuracy, which are equal to that of cross-roller rings. By adopting a new structure to change the rolling elements from rollers to balls, this product achieves the greatest high-speed performance ever offered by THK.
THK has developed its best-performing, high-speed rotary bearing ever: the High-Speed, Double-Row Angular Contact Ring BWH. This rotary bearing has balls aligned inside a cage between the inner and outer rings and is part of the THK Rotary Series, along with the cross-roller ring. The main features of this product are its ability to receive loads in all directions as well as its high rigidity and rotational accuracy, which are equal to that of cross-roller rings. By adopting a new structure to change the rolling elements from rollers to balls, this product achieves the greatest high-speed performance ever offered by THK.
Learn more.
Elevating tables: Precise vertical positioning in tight spaces
 As semicon-ductors and optical components become smaller and more sophisticated, the TZ Series of precision elevating tables from IKO International provides exceptional vertical positioning accuracy in a compact size. This unit features a unique wedge mechanism guided in the vertical direction by a pair of IKO C-Lube Super MX linear motion rolling guides arranged in parallel to achieve highly precise positioning with exceptional rigidity. An optional linear encoder provides full closed loop control to achieve positioning accuracy as high as 0.005 mm, with repeatability of +/-0.001 mm.
As semicon-ductors and optical components become smaller and more sophisticated, the TZ Series of precision elevating tables from IKO International provides exceptional vertical positioning accuracy in a compact size. This unit features a unique wedge mechanism guided in the vertical direction by a pair of IKO C-Lube Super MX linear motion rolling guides arranged in parallel to achieve highly precise positioning with exceptional rigidity. An optional linear encoder provides full closed loop control to achieve positioning accuracy as high as 0.005 mm, with repeatability of +/-0.001 mm.
Learn more and get all the specs.
This cobot is all about safety around people
 The COBOTTA PRO from DENSO Robotics is a lightweight, high-speed collaborative robot designed for communication between workers and robots while maximizing productivity. It delivers a blend of productivity and safety for both simple tasks and multi-step processes like assembly and inspection work. The 6-axis unit operates at speeds up to 2,500 mm per sec when no workers are near and slows or stops when people approach. Two models available: PRO 900 (max payload 6 kg) and PRO 1300 (max payload 12 kg). Many more functions and features.
The COBOTTA PRO from DENSO Robotics is a lightweight, high-speed collaborative robot designed for communication between workers and robots while maximizing productivity. It delivers a blend of productivity and safety for both simple tasks and multi-step processes like assembly and inspection work. The 6-axis unit operates at speeds up to 2,500 mm per sec when no workers are near and slows or stops when people approach. Two models available: PRO 900 (max payload 6 kg) and PRO 1300 (max payload 12 kg). Many more functions and features.
Learn more.
Powerful, pull-type clapper solenoids handle myriad jobs
 New powerful, low-profile, pull-type clapper solenoids are available from Magnetic Sensor Systems (MSS). Applications include valve control, locks, starters, ventilators, clamping, sorting, appliances, tools, HVAC, brakes, clutches, switches, mixing, fire suppression systems, door controls, detent latches, and more. The S-16-264 Series of 17 Pull-Type Clapper Solenoids have ampere turns (windings) adjusted to meet the specific force and duty cycle requirements of your application. They provide up to 130 lb (578 N) of force.
New powerful, low-profile, pull-type clapper solenoids are available from Magnetic Sensor Systems (MSS). Applications include valve control, locks, starters, ventilators, clamping, sorting, appliances, tools, HVAC, brakes, clutches, switches, mixing, fire suppression systems, door controls, detent latches, and more. The S-16-264 Series of 17 Pull-Type Clapper Solenoids have ampere turns (windings) adjusted to meet the specific force and duty cycle requirements of your application. They provide up to 130 lb (578 N) of force.
Get all the specs for these solenoids and other options.
Tech Tip: Belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator?
 Bishop-Wisecarver provides a quick, very useful guide to help you evaluate the right drive strategy for your system: belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator. Each drive type has unique advantages and limitations, so evaluating all your options will help you find the most suitable actuator setup for your specific application needs.
Bishop-Wisecarver provides a quick, very useful guide to help you evaluate the right drive strategy for your system: belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator. Each drive type has unique advantages and limitations, so evaluating all your options will help you find the most suitable actuator setup for your specific application needs.
Read the Bishop-Wisecarver blog.
Ultra-precise linear stage -- down to 0.005 microns
 PI, a global leader in precision motion control and nanoposi-tioning, now offers fast delivery of the L-511 linear micropositioning stage, which is designed for applications requiring minimum incremental motion down to 20 nm, drive forces up to 22 lb, and multi-axis configuration options. The L-511 can be combined to form XY or XYZ motion systems and integrated with rotary stages. A variety of drive and encoder options (stepper and servo motors, rotary, and linear encoders) enable ultra-fine sensitivity. Applications include: metrology, laser processing, semiconductors, biotech, optical alignment, and advanced automation.
PI, a global leader in precision motion control and nanoposi-tioning, now offers fast delivery of the L-511 linear micropositioning stage, which is designed for applications requiring minimum incremental motion down to 20 nm, drive forces up to 22 lb, and multi-axis configuration options. The L-511 can be combined to form XY or XYZ motion systems and integrated with rotary stages. A variety of drive and encoder options (stepper and servo motors, rotary, and linear encoders) enable ultra-fine sensitivity. Applications include: metrology, laser processing, semiconductors, biotech, optical alignment, and advanced automation.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Choosing the right stepper motor: PM or hybrid?
 According to the experts at Lin Engineering, there are two primary types of stepper motors to consider: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. But which is right for your application? Both types have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific requirements.
According to the experts at Lin Engineering, there are two primary types of stepper motors to consider: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. But which is right for your application? Both types have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific requirements.
Read this informative Lin Engineering article.
New PTFE-free linear guide for precise positioning
 The new drylin WWP linear guide from igus features a PTFE-free locking carriage. Engineered from lubrication-free, high-performance polymers and aluminum, the guide offers a lightweight, hygienic, and low-maintenance alternative to complex mechanical and electronic adjustment systems. It is significantly more compact and lightweight than conventional recirculating ball-bearing systems. Applications include interior components in vehicles, aircraft, and furniture.
The new drylin WWP linear guide from igus features a PTFE-free locking carriage. Engineered from lubrication-free, high-performance polymers and aluminum, the guide offers a lightweight, hygienic, and low-maintenance alternative to complex mechanical and electronic adjustment systems. It is significantly more compact and lightweight than conventional recirculating ball-bearing systems. Applications include interior components in vehicles, aircraft, and furniture.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Heavy-duty gear units for mixing and agitating systems
 MAXXDRIVE industrial gear units from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS are an established drive solution for heavy-duty applications. In addition to conveying, lifting, and driving, they also play an important role in mixing and agitating systems. MAXXDRIVE units feature a compact, one-piece UNICASE housing that delivers long service life, easy maintenance, and quiet operation. Their robust design handles high axial and radial loads, achieves output torques up to 2,495,900 lb-in., and powers up to 8,075 hp.
MAXXDRIVE industrial gear units from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS are an established drive solution for heavy-duty applications. In addition to conveying, lifting, and driving, they also play an important role in mixing and agitating systems. MAXXDRIVE units feature a compact, one-piece UNICASE housing that delivers long service life, easy maintenance, and quiet operation. Their robust design handles high axial and radial loads, achieves output torques up to 2,495,900 lb-in., and powers up to 8,075 hp.
Learn more.
What are non-captive linear actuators?
 According to PBC Linear, their new non-captive linear actuators are different from the more common external versions of lead screw-driven linear actuators because they allow the lead screw to completely pass through the motor. This fundamental difference offers advantages for designs that have limited space available or for engineers looking to shrink the overall size of their design package.
According to PBC Linear, their new non-captive linear actuators are different from the more common external versions of lead screw-driven linear actuators because they allow the lead screw to completely pass through the motor. This fundamental difference offers advantages for designs that have limited space available or for engineers looking to shrink the overall size of their design package.
Read the full PBC Linear blog.
Güdel introduces Swiss-quality tracks for cobots
 Güdel Inc. is highlighting new technologies at Automate 2025 booth #2418 that demonstrate its unmatched ability to solve automation engineering challenges. One is the Cobomover, a 7th-axis linear track purpose-built for collaborative and lightweight robots. Designed and manufactured in Switzerland, this unit extends the working range of robots up to 5 m, allowing them to operate multiple workstations and perform a variety of tasks without manual repositioning. Compatible with over 60 cobots and small traditional robots.
Güdel Inc. is highlighting new technologies at Automate 2025 booth #2418 that demonstrate its unmatched ability to solve automation engineering challenges. One is the Cobomover, a 7th-axis linear track purpose-built for collaborative and lightweight robots. Designed and manufactured in Switzerland, this unit extends the working range of robots up to 5 m, allowing them to operate multiple workstations and perform a variety of tasks without manual repositioning. Compatible with over 60 cobots and small traditional robots.
Learn more and get all the specs.
NASA awards $5 million to develop next-gen methane rocket engines
The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) has been awarded a $5 million grant from NASA to develop the next generation of rocket engines using liquid methane. The methane-based rocket technology would be used for in-space propulsion and ascent and descent engines for Mars and lunar landers.
Liquid methane, a new form of green propellant, is a promising fuel for spacecraft, according to Professor and Chair of Mechanical Engineering Ahsan Choudhuri, Ph.D., who is the project's principal investigator.
The development of methane rocket engines is identified as a critically enabling technology in the NASA Space Technology Roadmap. Human-Mars mission architectures point to a liquid oxygen-liquid methane (LO2/CH4) economy utilizing common reactants, created from scavenging the atmosphere and land via In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU). Due to the very high cost of getting mass to Mars, it is critical that the destination vehicles (e.g., landers) be very mass and volume efficient.
The research will be led by UTEP's NASA-funded Center for Space Exploration and Technology Research (cSETR), which is directed by Choudhuri. The total project cost is $9.3 million, which includes industry and institutional commitments of $4.3 million to continue to build an enduring aerospace research capacity at UTEP.
UTEP's cSETR has forged strategic partnerships with NASA Johnson Space Center, Marshall Space Flight Center, Glenn Research Center, White Sands Test Facility, Lockheed Martin Corp., Blue Origin, Orbital ATK, University of Maryland, and Princeton University to pursue its technical and educational goals.
"The cSETR's experienced and focused research activities in liquid oxygen-liquid methane propulsion have notably benefitted the Johnson Space Center engineering team in efforts to develop and demonstrate integrated liquid oxygen-liquid methane spacecraft solutions with relevance to human space flight," said Lauri N. Hansen, the director of engineering of NASA's Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center.
cSETR will focus on training 35 undergraduate and graduate students per year in space engineering education and research to increase the number of STEM degrees awarded, especially for underrepresented groups. The cSETR team also will partner with Savannah State University and Southern Arkansas University to create a student pipeline for UTEP engineering graduate programs.
Source: University of Texas at El Paso
Published June 2015
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

