 |
| August 02, 2016 | Volume 12 Issue 29 |
Motion Control News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Robots think and act on the fly at moving assembly line speeds
 Inbolt and FANUC are launching a manufacturing breakthrough enabling FANUC robots to tackle one of the most complex automation challenges: performing production tasks on continuously moving parts at line speeds. With Inbolt's AI-powered 3D vision, manufacturers can now automate screw insertion, bolt rundown, glue application, and other high-precision tasks on parts moving down the line without costly infrastructure investments or cycle time compromises.
Inbolt and FANUC are launching a manufacturing breakthrough enabling FANUC robots to tackle one of the most complex automation challenges: performing production tasks on continuously moving parts at line speeds. With Inbolt's AI-powered 3D vision, manufacturers can now automate screw insertion, bolt rundown, glue application, and other high-precision tasks on parts moving down the line without costly infrastructure investments or cycle time compromises.
Learn more.
Best high-speed rotary bearing in THK history
 THK has developed its best-performing, high-speed rotary bearing ever: the High-Speed, Double-Row Angular Contact Ring BWH. This rotary bearing has balls aligned inside a cage between the inner and outer rings and is part of the THK Rotary Series, along with the cross-roller ring. The main features of this product are its ability to receive loads in all directions as well as its high rigidity and rotational accuracy, which are equal to that of cross-roller rings. By adopting a new structure to change the rolling elements from rollers to balls, this product achieves the greatest high-speed performance ever offered by THK.
THK has developed its best-performing, high-speed rotary bearing ever: the High-Speed, Double-Row Angular Contact Ring BWH. This rotary bearing has balls aligned inside a cage between the inner and outer rings and is part of the THK Rotary Series, along with the cross-roller ring. The main features of this product are its ability to receive loads in all directions as well as its high rigidity and rotational accuracy, which are equal to that of cross-roller rings. By adopting a new structure to change the rolling elements from rollers to balls, this product achieves the greatest high-speed performance ever offered by THK.
Learn more.
Elevating tables: Precise vertical positioning in tight spaces
 As semicon-ductors and optical components become smaller and more sophisticated, the TZ Series of precision elevating tables from IKO International provides exceptional vertical positioning accuracy in a compact size. This unit features a unique wedge mechanism guided in the vertical direction by a pair of IKO C-Lube Super MX linear motion rolling guides arranged in parallel to achieve highly precise positioning with exceptional rigidity. An optional linear encoder provides full closed loop control to achieve positioning accuracy as high as 0.005 mm, with repeatability of +/-0.001 mm.
As semicon-ductors and optical components become smaller and more sophisticated, the TZ Series of precision elevating tables from IKO International provides exceptional vertical positioning accuracy in a compact size. This unit features a unique wedge mechanism guided in the vertical direction by a pair of IKO C-Lube Super MX linear motion rolling guides arranged in parallel to achieve highly precise positioning with exceptional rigidity. An optional linear encoder provides full closed loop control to achieve positioning accuracy as high as 0.005 mm, with repeatability of +/-0.001 mm.
Learn more and get all the specs.
This cobot is all about safety around people
 The COBOTTA PRO from DENSO Robotics is a lightweight, high-speed collaborative robot designed for communication between workers and robots while maximizing productivity. It delivers a blend of productivity and safety for both simple tasks and multi-step processes like assembly and inspection work. The 6-axis unit operates at speeds up to 2,500 mm per sec when no workers are near and slows or stops when people approach. Two models available: PRO 900 (max payload 6 kg) and PRO 1300 (max payload 12 kg). Many more functions and features.
The COBOTTA PRO from DENSO Robotics is a lightweight, high-speed collaborative robot designed for communication between workers and robots while maximizing productivity. It delivers a blend of productivity and safety for both simple tasks and multi-step processes like assembly and inspection work. The 6-axis unit operates at speeds up to 2,500 mm per sec when no workers are near and slows or stops when people approach. Two models available: PRO 900 (max payload 6 kg) and PRO 1300 (max payload 12 kg). Many more functions and features.
Learn more.
Powerful, pull-type clapper solenoids handle myriad jobs
 New powerful, low-profile, pull-type clapper solenoids are available from Magnetic Sensor Systems (MSS). Applications include valve control, locks, starters, ventilators, clamping, sorting, appliances, tools, HVAC, brakes, clutches, switches, mixing, fire suppression systems, door controls, detent latches, and more. The S-16-264 Series of 17 Pull-Type Clapper Solenoids have ampere turns (windings) adjusted to meet the specific force and duty cycle requirements of your application. They provide up to 130 lb (578 N) of force.
New powerful, low-profile, pull-type clapper solenoids are available from Magnetic Sensor Systems (MSS). Applications include valve control, locks, starters, ventilators, clamping, sorting, appliances, tools, HVAC, brakes, clutches, switches, mixing, fire suppression systems, door controls, detent latches, and more. The S-16-264 Series of 17 Pull-Type Clapper Solenoids have ampere turns (windings) adjusted to meet the specific force and duty cycle requirements of your application. They provide up to 130 lb (578 N) of force.
Get all the specs for these solenoids and other options.
Tech Tip: Belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator?
 Bishop-Wisecarver provides a quick, very useful guide to help you evaluate the right drive strategy for your system: belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator. Each drive type has unique advantages and limitations, so evaluating all your options will help you find the most suitable actuator setup for your specific application needs.
Bishop-Wisecarver provides a quick, very useful guide to help you evaluate the right drive strategy for your system: belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator. Each drive type has unique advantages and limitations, so evaluating all your options will help you find the most suitable actuator setup for your specific application needs.
Read the Bishop-Wisecarver blog.
Ultra-precise linear stage -- down to 0.005 microns
 PI, a global leader in precision motion control and nanoposi-tioning, now offers fast delivery of the L-511 linear micropositioning stage, which is designed for applications requiring minimum incremental motion down to 20 nm, drive forces up to 22 lb, and multi-axis configuration options. The L-511 can be combined to form XY or XYZ motion systems and integrated with rotary stages. A variety of drive and encoder options (stepper and servo motors, rotary, and linear encoders) enable ultra-fine sensitivity. Applications include: metrology, laser processing, semiconductors, biotech, optical alignment, and advanced automation.
PI, a global leader in precision motion control and nanoposi-tioning, now offers fast delivery of the L-511 linear micropositioning stage, which is designed for applications requiring minimum incremental motion down to 20 nm, drive forces up to 22 lb, and multi-axis configuration options. The L-511 can be combined to form XY or XYZ motion systems and integrated with rotary stages. A variety of drive and encoder options (stepper and servo motors, rotary, and linear encoders) enable ultra-fine sensitivity. Applications include: metrology, laser processing, semiconductors, biotech, optical alignment, and advanced automation.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Choosing the right stepper motor: PM or hybrid?
 According to the experts at Lin Engineering, there are two primary types of stepper motors to consider: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. But which is right for your application? Both types have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific requirements.
According to the experts at Lin Engineering, there are two primary types of stepper motors to consider: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. But which is right for your application? Both types have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific requirements.
Read this informative Lin Engineering article.
New PTFE-free linear guide for precise positioning
 The new drylin WWP linear guide from igus features a PTFE-free locking carriage. Engineered from lubrication-free, high-performance polymers and aluminum, the guide offers a lightweight, hygienic, and low-maintenance alternative to complex mechanical and electronic adjustment systems. It is significantly more compact and lightweight than conventional recirculating ball-bearing systems. Applications include interior components in vehicles, aircraft, and furniture.
The new drylin WWP linear guide from igus features a PTFE-free locking carriage. Engineered from lubrication-free, high-performance polymers and aluminum, the guide offers a lightweight, hygienic, and low-maintenance alternative to complex mechanical and electronic adjustment systems. It is significantly more compact and lightweight than conventional recirculating ball-bearing systems. Applications include interior components in vehicles, aircraft, and furniture.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Heavy-duty gear units for mixing and agitating systems
 MAXXDRIVE industrial gear units from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS are an established drive solution for heavy-duty applications. In addition to conveying, lifting, and driving, they also play an important role in mixing and agitating systems. MAXXDRIVE units feature a compact, one-piece UNICASE housing that delivers long service life, easy maintenance, and quiet operation. Their robust design handles high axial and radial loads, achieves output torques up to 2,495,900 lb-in., and powers up to 8,075 hp.
MAXXDRIVE industrial gear units from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS are an established drive solution for heavy-duty applications. In addition to conveying, lifting, and driving, they also play an important role in mixing and agitating systems. MAXXDRIVE units feature a compact, one-piece UNICASE housing that delivers long service life, easy maintenance, and quiet operation. Their robust design handles high axial and radial loads, achieves output torques up to 2,495,900 lb-in., and powers up to 8,075 hp.
Learn more.
What are non-captive linear actuators?
 According to PBC Linear, their new non-captive linear actuators are different from the more common external versions of lead screw-driven linear actuators because they allow the lead screw to completely pass through the motor. This fundamental difference offers advantages for designs that have limited space available or for engineers looking to shrink the overall size of their design package.
According to PBC Linear, their new non-captive linear actuators are different from the more common external versions of lead screw-driven linear actuators because they allow the lead screw to completely pass through the motor. This fundamental difference offers advantages for designs that have limited space available or for engineers looking to shrink the overall size of their design package.
Read the full PBC Linear blog.
Güdel introduces Swiss-quality tracks for cobots
 Güdel Inc. is highlighting new technologies at Automate 2025 booth #2418 that demonstrate its unmatched ability to solve automation engineering challenges. One is the Cobomover, a 7th-axis linear track purpose-built for collaborative and lightweight robots. Designed and manufactured in Switzerland, this unit extends the working range of robots up to 5 m, allowing them to operate multiple workstations and perform a variety of tasks without manual repositioning. Compatible with over 60 cobots and small traditional robots.
Güdel Inc. is highlighting new technologies at Automate 2025 booth #2418 that demonstrate its unmatched ability to solve automation engineering challenges. One is the Cobomover, a 7th-axis linear track purpose-built for collaborative and lightweight robots. Designed and manufactured in Switzerland, this unit extends the working range of robots up to 5 m, allowing them to operate multiple workstations and perform a variety of tasks without manual repositioning. Compatible with over 60 cobots and small traditional robots.
Learn more and get all the specs.
New open-center XYZ stage
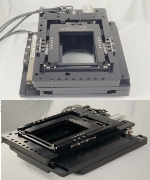 ThruSight-Focus is a high-performance, compact motion platform specifically engineered for applications requiring dual-side access to the sample or workpiece. It pairs ALIO's monolithic open-center XY stage -- known for its nanometer-level precision, crossed roller bearings, and direct linear drives -- with a novel Z-wedge mechanism that converts horizontal drive force into vertical motion via direct drive. This innovative architecture eliminates backlash, enhances servo responsiveness, and delivers fast, stable Z-axis movements -- all within a low-profile footprint.
ThruSight-Focus is a high-performance, compact motion platform specifically engineered for applications requiring dual-side access to the sample or workpiece. It pairs ALIO's monolithic open-center XY stage -- known for its nanometer-level precision, crossed roller bearings, and direct linear drives -- with a novel Z-wedge mechanism that converts horizontal drive force into vertical motion via direct drive. This innovative architecture eliminates backlash, enhances servo responsiveness, and delivers fast, stable Z-axis movements -- all within a low-profile footprint.
Learn more.
Eaton unveils differential engineered for EVs
 Intelligent power management company Eaton launched a new differential engineered specifically for electric vehicles at Auto Shanghai 2025 in China. The innovative design addresses the unique challenges presented by EV propulsion systems, including shared low-viscosity oil environments, increased sensitivity to noise, and the demands of high and instant torque delivery.
Intelligent power management company Eaton launched a new differential engineered specifically for electric vehicles at Auto Shanghai 2025 in China. The innovative design addresses the unique challenges presented by EV propulsion systems, including shared low-viscosity oil environments, increased sensitivity to noise, and the demands of high and instant torque delivery.
Read the full article.
Top Product: Integrated servo system is 20% smaller than standalone unit
 Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Read the full article.
Breakthrough solar cell captures CO2 and sunlight, produces burnable fuel
1,000-fold improved chemistry leads to "artificial leaf" that makes syngas.
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago have engineered a potentially game-changing solar cell that cheaply and efficiently converts atmospheric carbon dioxide directly into usable hydrocarbon fuel, using only sunlight for energy.
The finding is reported in the July 29 issue of Science and was funded by the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Energy. A provisional patent application has been filed.
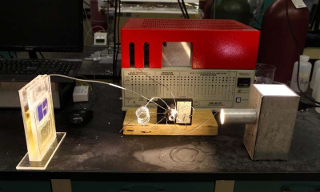
Simulated sunlight powers a solar cell that converts atmospheric carbon dioxide directly into syngas. [Credit: University of Illinois at Chicago/Jenny Fontaine]
Unlike conventional solar cells, which convert sunlight into electricity that must be stored in heavy batteries, the new device essentially does the work of plants, converting atmospheric carbon dioxide into fuel, solving two crucial problems at once. A solar farm of such "artificial leaves" could remove significant amounts of carbon from the atmosphere and produce energy-dense fuel efficiently.
"The new solar cell is not photovoltaic -- it's photosynthetic," says Amin Salehi-Khojin, assistant professor of mechanical and industrial engineering at UIC and senior author on the study.
"Instead of producing energy in an unsustainable one-way route from fossil fuels to greenhouse gas, we can now reverse the process and recycle atmospheric carbon into fuel using sunlight," he said.
While plants produce fuel in the form of sugar, the artificial leaf delivers syngas, or synthesis gas, a mixture of hydrogen gas and carbon monoxide. Syngas can be burned directly, or converted into diesel or other hydrocarbon fuels.
The ability to turn CO2 into fuel at a cost comparable to a gallon of gasoline would render fossil fuels obsolete.
Chemical reactions that convert CO2 into burnable forms of carbon are called reduction reactions, the opposite of oxidation or combustion. Engineers have been exploring different catalysts to drive CO2 reduction, but so far such reactions have been inefficient and rely on expensive precious metals such as silver, Salehi-Khojin said.
"What we needed was a new family of chemicals with extraordinary properties," he said.
Salehi-Khojin and his coworkers focused on a family of nano-structured compounds called transition metal dichalcogenides -- or TMDCs -- as catalysts, pairing them with an unconventional ionic liquid as the electrolyte inside a two-compartment, three-electrode electrochemical cell.
The best of several catalysts they studied turned out to be nanoflake tungsten diselenide.
"The new catalyst is more active; more able to break carbon dioxide's chemical bonds," said UIC postdoctoral researcher Mohammad Asadi, first author on the Science paper.
In fact, he said, the new catalyst is 1,000 times faster than noble-metal catalysts -- and about 20 times cheaper.
Other researchers have used TMDC catalysts to produce hydrogen by other means, but not by reduction of CO2. The catalyst couldn't survive the reaction.
"The active sites of the catalyst get poisoned and oxidized," Salehi-Khojin said. The breakthrough, he said, was to use an ionic fluid called ethyl-methyl-imidazolium tetrafluoroborate, mixed 50-50 with water.
"The combination of water and the ionic liquid makes a co-catalyst that preserves the catalyst's active sites under the harsh reduction reaction conditions," Salehi-Khojin said.
The UIC artificial leaf consists of two silicon triple-junction photovoltaic cells of 18 cm2 to harvest light; the tungsten diselenide and ionic liquid co-catalyst system on the cathode side; and cobalt oxide in potassium phosphate electrolyte on the anode side.
When light of 100 watts per square meter -- about the average intensity reaching the Earth's surface -- energizes the cell, hydrogen and carbon monoxide gas bubble up from the cathode, while free oxygen and hydrogen ions are produced at the anode.
"The hydrogen ions diffuse through a membrane to the cathode side, to participate in the carbon dioxide reduction reaction," said Asadi.
The technology should be adaptable not only to large-scale use, like solar farms, but also to small-scale applications, Salehi-Khojin said. In the future, he said, it may prove useful on Mars, where the atmosphere is mostly carbon dioxide, if the planet is also found to have water.
"Nanostructured transition metal dichalcogenide electrocatalysts for CO2 reduction in ionic liquid" is online at http://www.eurekalert.org/jrnls/sci/ or by contacting scipak@aaas.org.
Co-authors with Asadi and Salehi-Khojin are Kibum Kim, Aditya Venkata Addepalli, Pedram Abbasi, Poya Yasaei, Amirhossein Behranginia, Bijandra Kumar and Jeremiah Abiade of UIC's mechanical and industrial engineering department, who performed the electrochemical experiments and prepared the catalyst under NSF contract CBET-1512647; Robert F. Klie and Patrick Phillips of UIC's physics department, who performed electron microscopy and spectroscopy experiments; Larry A. Curtiss, Cong Liu and Peter Zapol of Argonne National Laboratory, who did Density Functional Theory calculations under DOE contract DE-ACO206CH11357; Richard Haasch of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, who did ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy; and Josť M. Cerrato of the University of New Mexico, who did elemental analysis.
Source: University of Illinois at Chicago
Published August 2016
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

