 |
| March 05, 2019 | Volume 15 Issue 09 |
Motion Control News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Robots think and act on the fly at moving assembly line speeds
 Inbolt and FANUC are launching a manufacturing breakthrough enabling FANUC robots to tackle one of the most complex automation challenges: performing production tasks on continuously moving parts at line speeds. With Inbolt's AI-powered 3D vision, manufacturers can now automate screw insertion, bolt rundown, glue application, and other high-precision tasks on parts moving down the line without costly infrastructure investments or cycle time compromises.
Inbolt and FANUC are launching a manufacturing breakthrough enabling FANUC robots to tackle one of the most complex automation challenges: performing production tasks on continuously moving parts at line speeds. With Inbolt's AI-powered 3D vision, manufacturers can now automate screw insertion, bolt rundown, glue application, and other high-precision tasks on parts moving down the line without costly infrastructure investments or cycle time compromises.
Learn more.
Best high-speed rotary bearing in THK history
 THK has developed its best-performing, high-speed rotary bearing ever: the High-Speed, Double-Row Angular Contact Ring BWH. This rotary bearing has balls aligned inside a cage between the inner and outer rings and is part of the THK Rotary Series, along with the cross-roller ring. The main features of this product are its ability to receive loads in all directions as well as its high rigidity and rotational accuracy, which are equal to that of cross-roller rings. By adopting a new structure to change the rolling elements from rollers to balls, this product achieves the greatest high-speed performance ever offered by THK.
THK has developed its best-performing, high-speed rotary bearing ever: the High-Speed, Double-Row Angular Contact Ring BWH. This rotary bearing has balls aligned inside a cage between the inner and outer rings and is part of the THK Rotary Series, along with the cross-roller ring. The main features of this product are its ability to receive loads in all directions as well as its high rigidity and rotational accuracy, which are equal to that of cross-roller rings. By adopting a new structure to change the rolling elements from rollers to balls, this product achieves the greatest high-speed performance ever offered by THK.
Learn more.
Elevating tables: Precise vertical positioning in tight spaces
 As semicon-ductors and optical components become smaller and more sophisticated, the TZ Series of precision elevating tables from IKO International provides exceptional vertical positioning accuracy in a compact size. This unit features a unique wedge mechanism guided in the vertical direction by a pair of IKO C-Lube Super MX linear motion rolling guides arranged in parallel to achieve highly precise positioning with exceptional rigidity. An optional linear encoder provides full closed loop control to achieve positioning accuracy as high as 0.005 mm, with repeatability of +/-0.001 mm.
As semicon-ductors and optical components become smaller and more sophisticated, the TZ Series of precision elevating tables from IKO International provides exceptional vertical positioning accuracy in a compact size. This unit features a unique wedge mechanism guided in the vertical direction by a pair of IKO C-Lube Super MX linear motion rolling guides arranged in parallel to achieve highly precise positioning with exceptional rigidity. An optional linear encoder provides full closed loop control to achieve positioning accuracy as high as 0.005 mm, with repeatability of +/-0.001 mm.
Learn more and get all the specs.
This cobot is all about safety around people
 The COBOTTA PRO from DENSO Robotics is a lightweight, high-speed collaborative robot designed for communication between workers and robots while maximizing productivity. It delivers a blend of productivity and safety for both simple tasks and multi-step processes like assembly and inspection work. The 6-axis unit operates at speeds up to 2,500 mm per sec when no workers are near and slows or stops when people approach. Two models available: PRO 900 (max payload 6 kg) and PRO 1300 (max payload 12 kg). Many more functions and features.
The COBOTTA PRO from DENSO Robotics is a lightweight, high-speed collaborative robot designed for communication between workers and robots while maximizing productivity. It delivers a blend of productivity and safety for both simple tasks and multi-step processes like assembly and inspection work. The 6-axis unit operates at speeds up to 2,500 mm per sec when no workers are near and slows or stops when people approach. Two models available: PRO 900 (max payload 6 kg) and PRO 1300 (max payload 12 kg). Many more functions and features.
Learn more.
Powerful, pull-type clapper solenoids handle myriad jobs
 New powerful, low-profile, pull-type clapper solenoids are available from Magnetic Sensor Systems (MSS). Applications include valve control, locks, starters, ventilators, clamping, sorting, appliances, tools, HVAC, brakes, clutches, switches, mixing, fire suppression systems, door controls, detent latches, and more. The S-16-264 Series of 17 Pull-Type Clapper Solenoids have ampere turns (windings) adjusted to meet the specific force and duty cycle requirements of your application. They provide up to 130 lb (578 N) of force.
New powerful, low-profile, pull-type clapper solenoids are available from Magnetic Sensor Systems (MSS). Applications include valve control, locks, starters, ventilators, clamping, sorting, appliances, tools, HVAC, brakes, clutches, switches, mixing, fire suppression systems, door controls, detent latches, and more. The S-16-264 Series of 17 Pull-Type Clapper Solenoids have ampere turns (windings) adjusted to meet the specific force and duty cycle requirements of your application. They provide up to 130 lb (578 N) of force.
Get all the specs for these solenoids and other options.
Tech Tip: Belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator?
 Bishop-Wisecarver provides a quick, very useful guide to help you evaluate the right drive strategy for your system: belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator. Each drive type has unique advantages and limitations, so evaluating all your options will help you find the most suitable actuator setup for your specific application needs.
Bishop-Wisecarver provides a quick, very useful guide to help you evaluate the right drive strategy for your system: belt, screw, or chain-driven actuator. Each drive type has unique advantages and limitations, so evaluating all your options will help you find the most suitable actuator setup for your specific application needs.
Read the Bishop-Wisecarver blog.
Ultra-precise linear stage -- down to 0.005 microns
 PI, a global leader in precision motion control and nanoposi-tioning, now offers fast delivery of the L-511 linear micropositioning stage, which is designed for applications requiring minimum incremental motion down to 20 nm, drive forces up to 22 lb, and multi-axis configuration options. The L-511 can be combined to form XY or XYZ motion systems and integrated with rotary stages. A variety of drive and encoder options (stepper and servo motors, rotary, and linear encoders) enable ultra-fine sensitivity. Applications include: metrology, laser processing, semiconductors, biotech, optical alignment, and advanced automation.
PI, a global leader in precision motion control and nanoposi-tioning, now offers fast delivery of the L-511 linear micropositioning stage, which is designed for applications requiring minimum incremental motion down to 20 nm, drive forces up to 22 lb, and multi-axis configuration options. The L-511 can be combined to form XY or XYZ motion systems and integrated with rotary stages. A variety of drive and encoder options (stepper and servo motors, rotary, and linear encoders) enable ultra-fine sensitivity. Applications include: metrology, laser processing, semiconductors, biotech, optical alignment, and advanced automation.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Choosing the right stepper motor: PM or hybrid?
 According to the experts at Lin Engineering, there are two primary types of stepper motors to consider: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. But which is right for your application? Both types have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific requirements.
According to the experts at Lin Engineering, there are two primary types of stepper motors to consider: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. But which is right for your application? Both types have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific requirements.
Read this informative Lin Engineering article.
New PTFE-free linear guide for precise positioning
 The new drylin WWP linear guide from igus features a PTFE-free locking carriage. Engineered from lubrication-free, high-performance polymers and aluminum, the guide offers a lightweight, hygienic, and low-maintenance alternative to complex mechanical and electronic adjustment systems. It is significantly more compact and lightweight than conventional recirculating ball-bearing systems. Applications include interior components in vehicles, aircraft, and furniture.
The new drylin WWP linear guide from igus features a PTFE-free locking carriage. Engineered from lubrication-free, high-performance polymers and aluminum, the guide offers a lightweight, hygienic, and low-maintenance alternative to complex mechanical and electronic adjustment systems. It is significantly more compact and lightweight than conventional recirculating ball-bearing systems. Applications include interior components in vehicles, aircraft, and furniture.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Heavy-duty gear units for mixing and agitating systems
 MAXXDRIVE industrial gear units from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS are an established drive solution for heavy-duty applications. In addition to conveying, lifting, and driving, they also play an important role in mixing and agitating systems. MAXXDRIVE units feature a compact, one-piece UNICASE housing that delivers long service life, easy maintenance, and quiet operation. Their robust design handles high axial and radial loads, achieves output torques up to 2,495,900 lb-in., and powers up to 8,075 hp.
MAXXDRIVE industrial gear units from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS are an established drive solution for heavy-duty applications. In addition to conveying, lifting, and driving, they also play an important role in mixing and agitating systems. MAXXDRIVE units feature a compact, one-piece UNICASE housing that delivers long service life, easy maintenance, and quiet operation. Their robust design handles high axial and radial loads, achieves output torques up to 2,495,900 lb-in., and powers up to 8,075 hp.
Learn more.
What are non-captive linear actuators?
 According to PBC Linear, their new non-captive linear actuators are different from the more common external versions of lead screw-driven linear actuators because they allow the lead screw to completely pass through the motor. This fundamental difference offers advantages for designs that have limited space available or for engineers looking to shrink the overall size of their design package.
According to PBC Linear, their new non-captive linear actuators are different from the more common external versions of lead screw-driven linear actuators because they allow the lead screw to completely pass through the motor. This fundamental difference offers advantages for designs that have limited space available or for engineers looking to shrink the overall size of their design package.
Read the full PBC Linear blog.
Güdel introduces Swiss-quality tracks for cobots
 Güdel Inc. is highlighting new technologies at Automate 2025 booth #2418 that demonstrate its unmatched ability to solve automation engineering challenges. One is the Cobomover, a 7th-axis linear track purpose-built for collaborative and lightweight robots. Designed and manufactured in Switzerland, this unit extends the working range of robots up to 5 m, allowing them to operate multiple workstations and perform a variety of tasks without manual repositioning. Compatible with over 60 cobots and small traditional robots.
Güdel Inc. is highlighting new technologies at Automate 2025 booth #2418 that demonstrate its unmatched ability to solve automation engineering challenges. One is the Cobomover, a 7th-axis linear track purpose-built for collaborative and lightweight robots. Designed and manufactured in Switzerland, this unit extends the working range of robots up to 5 m, allowing them to operate multiple workstations and perform a variety of tasks without manual repositioning. Compatible with over 60 cobots and small traditional robots.
Learn more and get all the specs.
New open-center XYZ stage
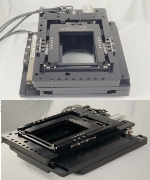 ThruSight-Focus is a high-performance, compact motion platform specifically engineered for applications requiring dual-side access to the sample or workpiece. It pairs ALIO's monolithic open-center XY stage -- known for its nanometer-level precision, crossed roller bearings, and direct linear drives -- with a novel Z-wedge mechanism that converts horizontal drive force into vertical motion via direct drive. This innovative architecture eliminates backlash, enhances servo responsiveness, and delivers fast, stable Z-axis movements -- all within a low-profile footprint.
ThruSight-Focus is a high-performance, compact motion platform specifically engineered for applications requiring dual-side access to the sample or workpiece. It pairs ALIO's monolithic open-center XY stage -- known for its nanometer-level precision, crossed roller bearings, and direct linear drives -- with a novel Z-wedge mechanism that converts horizontal drive force into vertical motion via direct drive. This innovative architecture eliminates backlash, enhances servo responsiveness, and delivers fast, stable Z-axis movements -- all within a low-profile footprint.
Learn more.
Eaton unveils differential engineered for EVs
 Intelligent power management company Eaton launched a new differential engineered specifically for electric vehicles at Auto Shanghai 2025 in China. The innovative design addresses the unique challenges presented by EV propulsion systems, including shared low-viscosity oil environments, increased sensitivity to noise, and the demands of high and instant torque delivery.
Intelligent power management company Eaton launched a new differential engineered specifically for electric vehicles at Auto Shanghai 2025 in China. The innovative design addresses the unique challenges presented by EV propulsion systems, including shared low-viscosity oil environments, increased sensitivity to noise, and the demands of high and instant torque delivery.
Read the full article.
Top Product: Integrated servo system is 20% smaller than standalone unit
 Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Read the full article.
700,000 submunitions demilitarized by Sandia-designed robotics system

Sandia National Laboratories scientists built and programmed an automated robotic system at the Anniston Munitions Center in Alabama to demilitarize Multiple Launch Rocket System submunitions for the Army. [Photo by Regina Valenzuela]
More than 700,000 Multiple Launch Rocket System submunitions have been demilitarized since the Army started using an automated nine-robot system conceptualized, built, and programmed by Sandia National Laboratories engineers.
"This is by far the most complex, automated robotic demilitarization system that Sandia has built in the last 20 years," said computer scientist Bill Prentice, Sandia software lead for the project. "This is exactly the kind of thing to use robotics for -- to get humans out of harm's way. Let the automation of robots do what they do well, and have humans make advanced decisions on safety."
The automated system, owned by the Army, is located at the Anniston Munitions Center's Multiple Launch Rocket System Recycle Facility in Alabama. The system was built for the Army's demilitarization program that aims to dismantle obsolete ammunition and missiles. The project was funded and managed through the Department of Defense.
The system safely reduces the stockpile of Multiple Launch Rocket System munitions that have been in storage, and it enables the Army to recycle rocket materials -- capabilities that did not exist. The Army can now recycle the rockets' aluminum warhead skin, steel grenade bodies, and copper.

Speeding up the process of demilitarization also reduces costs. The automated robotic system is designed to demilitarize up to 21 warheads per eight-hour shift.
"We were able to remove people from a potentially very dangerous situation and created something that allowed products to be recycled and reused, which is what the DOD demilitarization program is about," said project lead Walt Wapman, a mechanical engineer.
Humans still oversee operations, learn to run the advanced robotics system, and watch the process on live feeds in a control room. Computer vision, which is a form of artificial intelligence using digital images from cameras, can detect abnormalities during the demilitarization process and alert operators who determine if there is a safety concern.
How the system works
All system robots are commercial off-the-shelf robots that were customized and programmed by Sandia engineers to do specific tasks.
"There are 644 grenades per warhead, and our job is to take these tightly packed, columnated grenades in the warhead foam packs and demilitarize them," Prentice said.
The system is organized into nine "cells." The first cell is the weapons disassembly system where warheads are cut into separate foam pack sections. The foam packs filled with grenades are then delivered to cells 2 and 3, where the grenades are removed from the foam packs. From there, individual grenades are delivered to cells 4 through 9, where the fuses are detached. Once the fuses are detached, the munitions have been disarmed.
The system can pick up and place foam packs and grenades in precise orientations, and lock and rotate the grenades to examine and remove fuses in a safe way, Prentice said.

This automated system demilitarizes warheads by cutting them into separate sections, removing foam packs filled with grenades, and detaching grenade fuses. [Photo by Regina Valenzuela]
For more than three years, Prentice said he put his heart and soul into the robotic system. He and a small team used three computer languages to program the nine robot cells, tested the system, and traveled back and forth to Alabama while the robotic work cells were assembled and tested.
"Part of the challenge is when you demilitarize warheads like this, you're working on munitions that are 10, 20, 30 years old," Prentice said. "You test on inert munitions that are in pristine condition, but when you start cutting apart warheads and looking at live grenades, they might have some environmental effects that cause process abnormalities, such as grenades being stuck together during removal."
System is part of Sandia's long robotics history
Prentice said Sandia has been involved in robotics for more than 20 years and the demilitarization business for at least 18 years. Wapman led the demilitarization program at Sandia for most of that time.
"I'd say that what Sandia really brought to the table was an integrated, small team that took a blank sheet of paper and made a nine-robot automated system with 55 cameras, hundreds of sensors, and a lot of exceptional designs, enabling us to deliver a reliable system to the Army that's been safe," Wapman said.
Sandia National Laboratories is a multimission laboratory operated by National Technology and Engineering Solutions of Sandia LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Honeywell International Inc., for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
Source: Sandia
Published March 2019
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

