 |
| July 02, 2019 | Volume 15 Issue 25 |
Electrical/Electronic News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Isolated probing tech for fast-switching power device testing
 Keysight Technologies has developed an optically isolated differential probing family dedicated to enhancing efficiency and performance testing of fast-switching devices such as wide-bandgap GaN and SiC semiconductors. Validation of floating half-bridge and full-bridge architectures commonly used in power conversion, motor drives, and inverters requires measurement of small differential signals riding on high common-mode voltages. This measurement can be challenging due to voltage source fluctuations relative to ground, noise interference, and safety concerns.
Keysight Technologies has developed an optically isolated differential probing family dedicated to enhancing efficiency and performance testing of fast-switching devices such as wide-bandgap GaN and SiC semiconductors. Validation of floating half-bridge and full-bridge architectures commonly used in power conversion, motor drives, and inverters requires measurement of small differential signals riding on high common-mode voltages. This measurement can be challenging due to voltage source fluctuations relative to ground, noise interference, and safety concerns.
Learn more.
Protect sensitive electronics in explosive environments with new aluminum ATEX Cabinet Cooler Systems
 EXAIR's ATEX Cabinet Cooler® Systems deliver a powerful and affordable solution for keeping electrical enclosures cool in hazardous ATEX classified areas -- and they're now available in durable aluminum construction. Engineered for use in Zones 2 and 22, these coolers are UL tested, CE compliant, and meet stringent ATEX standards for purged and pressurized enclosures. With cooling capacities up to 5,600 Btu/Hr., ATEX Cabinet Coolers are ideal for preventing overheating in electrical cabinets. EXAIR offers a comprehensive lineup of systems.
EXAIR's ATEX Cabinet Cooler® Systems deliver a powerful and affordable solution for keeping electrical enclosures cool in hazardous ATEX classified areas -- and they're now available in durable aluminum construction. Engineered for use in Zones 2 and 22, these coolers are UL tested, CE compliant, and meet stringent ATEX standards for purged and pressurized enclosures. With cooling capacities up to 5,600 Btu/Hr., ATEX Cabinet Coolers are ideal for preventing overheating in electrical cabinets. EXAIR offers a comprehensive lineup of systems.
Learn more.
PLC handbook chock full of must-know information
 Automation-Direct's Practical Guide to Program-mable Logic Controllers Handbook has been improved with tons of new need-to-know info, making it a more comprehensive guide to the world of PLCs. Besides covering the basics of PLC history, PLC hardware, and PLC software, this guide takes you deeper into the ever-changing world of PLC communication, the importance of feedback loops, cyber security, and many other areas that are a must-know for any PLC novice or seasoned automation professional.
Automation-Direct's Practical Guide to Program-mable Logic Controllers Handbook has been improved with tons of new need-to-know info, making it a more comprehensive guide to the world of PLCs. Besides covering the basics of PLC history, PLC hardware, and PLC software, this guide takes you deeper into the ever-changing world of PLC communication, the importance of feedback loops, cyber security, and many other areas that are a must-know for any PLC novice or seasoned automation professional.
Get this great resource today.
Haptic feedback prototyping kit from TDK
 Get your customers to feel the difference your products make. TDK has released a development starter kit for fast haptics prototyping. It gives mechanical designers and engineers first impressions of the haptic feedback using PowerHap piezo actuators, shows how the mechanical integration works, and provides a reference design. Applications include automotive, displays and tablets, household appliances, vending machines, game controllers, industrial equipment, and medical devices.
Get your customers to feel the difference your products make. TDK has released a development starter kit for fast haptics prototyping. It gives mechanical designers and engineers first impressions of the haptic feedback using PowerHap piezo actuators, shows how the mechanical integration works, and provides a reference design. Applications include automotive, displays and tablets, household appliances, vending machines, game controllers, industrial equipment, and medical devices.
Learn more.
Mini ESD preset torque screwdriver
 Need precision fastening with ESD protection at the smallest torque levels? Mountz has you covered. The new FG Mini ESD Preset Torque Screwdriver is built for low-torque, high-precision tasks. Its compact design makes it ideal for tight spaces and small fasteners, while delivering the same reliable control and ESD protection users have come to expect from Mountz. Two models available: FG25z (3 to 25 ozf.in, 2 to 17.7 cN-m) and FG50z (20 to 50 ozf.in, 14.1 to 35.3 cN-m).
Need precision fastening with ESD protection at the smallest torque levels? Mountz has you covered. The new FG Mini ESD Preset Torque Screwdriver is built for low-torque, high-precision tasks. Its compact design makes it ideal for tight spaces and small fasteners, while delivering the same reliable control and ESD protection users have come to expect from Mountz. Two models available: FG25z (3 to 25 ozf.in, 2 to 17.7 cN-m) and FG50z (20 to 50 ozf.in, 14.1 to 35.3 cN-m).
Learn more.
Laumas load cells and electronics from AutomationDirect
 Automation-Direct has added Laumas precision-engineered load cells, transmitters, and accessories that deliver reliable performance in industrial weighing and force measurement applications. The FCAL series high-precision bending beam load cells are ideal for low- to mid-capacity systems. CTL series load cells are designed for both tension and compression, with excellent linearity. The CBL series low-profile compression load cells are perfect for space-limited applications. Laumas load cell transmitters are available too for precise monitoring and control. Very good pricing.
Automation-Direct has added Laumas precision-engineered load cells, transmitters, and accessories that deliver reliable performance in industrial weighing and force measurement applications. The FCAL series high-precision bending beam load cells are ideal for low- to mid-capacity systems. CTL series load cells are designed for both tension and compression, with excellent linearity. The CBL series low-profile compression load cells are perfect for space-limited applications. Laumas load cell transmitters are available too for precise monitoring and control. Very good pricing.
Learn more.
Engineer's Toolbox: What is ground loop feedback?
 Improper grounding can create problems in data logging, data acquisition, and measurement and control systems. One of the most common problems is known as ground loop feedback. Experts at CAS DataLoggers run through five ways to eliminate this problem.
Improper grounding can create problems in data logging, data acquisition, and measurement and control systems. One of the most common problems is known as ground loop feedback. Experts at CAS DataLoggers run through five ways to eliminate this problem.
Read the full article.
What is a braking resistor?
 According to Automation-Direct, "Braking resistors don't actually provide braking directly -- rather, they allow a drive to stop a loaded motor faster." Why is this important? Protect your AC or DC drive system from regenerative voltage that can create an over-voltage fault on the drive -- especially with high inertial loads or rapid deceleration.
According to Automation-Direct, "Braking resistors don't actually provide braking directly -- rather, they allow a drive to stop a loaded motor faster." Why is this important? Protect your AC or DC drive system from regenerative voltage that can create an over-voltage fault on the drive -- especially with high inertial loads or rapid deceleration.
View the video.
New Digital Static Meter: Precise measurement, easy use
 Static electricity isn't just a nuisance; it's a serious threat to manufacturing efficiency, product integrity, and workplace safety. Unchecked static can lead to costly downtime, product defects, material jams, and even hazardous shocks to employees. If static is interfering with your processes, EXAIR's upgraded Model 7905 Digital Static Meter offers an essential first step in identifying and eliminating the problem. With just the press of a button, this easy-to-use, handheld device pinpoints the highest voltage areas in your facility, helping you diagnose static issues before they become a problem.
Static electricity isn't just a nuisance; it's a serious threat to manufacturing efficiency, product integrity, and workplace safety. Unchecked static can lead to costly downtime, product defects, material jams, and even hazardous shocks to employees. If static is interfering with your processes, EXAIR's upgraded Model 7905 Digital Static Meter offers an essential first step in identifying and eliminating the problem. With just the press of a button, this easy-to-use, handheld device pinpoints the highest voltage areas in your facility, helping you diagnose static issues before they become a problem.
Learn more.
New laser cutting modulating strategy tested with Mikrotron high-speed camera
 Modulating a laser beam's intensity distribution optimizes energy delivery to the process zone, resulting in better cutting speed, cut edge quality, and cut kerf geometry. Scientists in Belgium have come up with a new method that they say produces better cutting results.
Modulating a laser beam's intensity distribution optimizes energy delivery to the process zone, resulting in better cutting speed, cut edge quality, and cut kerf geometry. Scientists in Belgium have come up with a new method that they say produces better cutting results.
Read the full article.
All-in-one embedded PLC based on Raspberry Pi 4 -- build control applications
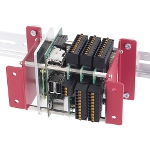 The new PLC CPI-PS10CM4 from Contec Co. is a compact embedded programmable logic controller (PLC) that is loaded with CODESYS, the world's most widely used software PLC. This product uses Contec's original single-board computer, which is based on Raspberry Pi's latest embedded module, the Compute Module 4 (CM4). By using the wide range of peripheral devices for Raspberry Pi, such as Contec's CPI Series, you can build various control applications in a PLC language that complies with the IEC 61131-3 international standard.
The new PLC CPI-PS10CM4 from Contec Co. is a compact embedded programmable logic controller (PLC) that is loaded with CODESYS, the world's most widely used software PLC. This product uses Contec's original single-board computer, which is based on Raspberry Pi's latest embedded module, the Compute Module 4 (CM4). By using the wide range of peripheral devices for Raspberry Pi, such as Contec's CPI Series, you can build various control applications in a PLC language that complies with the IEC 61131-3 international standard.
Learn more.
Torque sensors for fastening applications and more
 Saelig Company has introduced the Sensor Technology SGR525/526 Series Torque Sensors to provide precision torque monitoring that is critical for performance and safety. The square drive design (for applications with non-cylindrical shafts) allows for seamless integration into power tools, test rigs, industrial machinery, and precision fastening applications, ensuring superior torque measurement without the need for additional adapters or modifications. The SGR525 offers torque measurement only, while the SGR526 provides torque, speed, and power measurement using a 360-pulse-per-revolution encoder. Industries include automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and research and development.
Saelig Company has introduced the Sensor Technology SGR525/526 Series Torque Sensors to provide precision torque monitoring that is critical for performance and safety. The square drive design (for applications with non-cylindrical shafts) allows for seamless integration into power tools, test rigs, industrial machinery, and precision fastening applications, ensuring superior torque measurement without the need for additional adapters or modifications. The SGR525 offers torque measurement only, while the SGR526 provides torque, speed, and power measurement using a 360-pulse-per-revolution encoder. Industries include automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and research and development.
Learn more.
Wide-angle camera optimized for larger, faster conveyor belts
 Wider conveyor belts operating at higher speeds are now commonplace in modern logistics. To keep up, SVS-Vistek is offering a cost-effective alternative to multi-camera systems with its fxo901CXGE 10-GigE color camera featuring the Sony IMX901-AQR wide-aspect global shutter 16.4-megapixel CMOS sensor. Unlike standard cameras, this unit captures targets in a wide field of view while maintaining high resolutions. The 4:1 horizontal aspect ratio allows one fxo901CXGE to replace an entire multi-camera system, removing the need for image synchronization.
Wider conveyor belts operating at higher speeds are now commonplace in modern logistics. To keep up, SVS-Vistek is offering a cost-effective alternative to multi-camera systems with its fxo901CXGE 10-GigE color camera featuring the Sony IMX901-AQR wide-aspect global shutter 16.4-megapixel CMOS sensor. Unlike standard cameras, this unit captures targets in a wide field of view while maintaining high resolutions. The 4:1 horizontal aspect ratio allows one fxo901CXGE to replace an entire multi-camera system, removing the need for image synchronization.
Learn more.
Handheld thermal imager cuts diagnostic time
 The FLIR TG268 is a next-generation thermal imager that provides professionals in the utility, manufacturing, electrical, automotive, and industrial sectors with a lightweight, handheld, affordable condition monitoring tool. Latest enhancements include higher temperature ranges, improved resolution, and larger data storage capacity. Go beyond the restrictions of single-spot IR thermometers to view and evaluate hot and cold spots that may signify potentially dangerous issues. Accurately measure temps from -25 to 400 C. Native thermal images improved with Super Resolution upscaling.
The FLIR TG268 is a next-generation thermal imager that provides professionals in the utility, manufacturing, electrical, automotive, and industrial sectors with a lightweight, handheld, affordable condition monitoring tool. Latest enhancements include higher temperature ranges, improved resolution, and larger data storage capacity. Go beyond the restrictions of single-spot IR thermometers to view and evaluate hot and cold spots that may signify potentially dangerous issues. Accurately measure temps from -25 to 400 C. Native thermal images improved with Super Resolution upscaling.
Learn more.
SOLIDWORKS 2025: Sheet metal design top features from an expert
 Find out what's new in SOLIDWORKS 2025 when it comes to sheet metal and weldments, and learn some valuable tips and tricks along the way from TriMech. Topics covered include copying cut list properties, bend notches, tab and slot enhancements, groove beads (a new type of weld bead), performance enhancements, and more. When you're done, check out TriMech's full YouTube channel filled with educational material.
Find out what's new in SOLIDWORKS 2025 when it comes to sheet metal and weldments, and learn some valuable tips and tricks along the way from TriMech. Topics covered include copying cut list properties, bend notches, tab and slot enhancements, groove beads (a new type of weld bead), performance enhancements, and more. When you're done, check out TriMech's full YouTube channel filled with educational material.
View the video.
Scientists break record for highest temperature superconductor
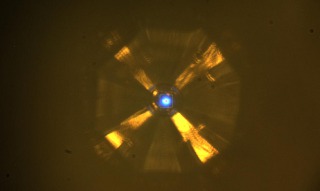
Scientists bombarded a sample of a new superconducting material (center) with X-rays to study its structure at the Advanced Photon Source.
University of Chicago scientists are part of an international research team that has discovered superconductivity -- the ability to conduct electricity perfectly -- at the highest temperatures ever recorded.
Using advanced technology at UChicago-affiliated Argonne National Laboratory, the team studied a class of materials in which they observed superconductivity at temperatures of about -23 C (-9 F) -- a jump of about 50 degrees compared to the previous confirmed record.
Though the superconductivity happened under extremely high pressure, the result still represents a big step toward creating superconductivity at room temperature -- the ultimate goal for scientists to be able to use this phenomenon for advanced technologies. The results were published May 22 in the journal Nature; Vitali Prakapenka, a research professor at the University of Chicago, and Eran Greenberg, a postdoctoral scholar at the University of Chicago, are co-authors of the research.
Just as a copper wire conducts electricity better than a rubber tube, certain kinds of materials are better at becoming superconductive, a state defined by two main properties: The material offers zero resistance to electrical current and cannot be penetrated by magnetic fields. The potential uses for this are as vast as they are exciting: electrical wires without diminishing currents, extremely fast supercomputers, and efficient magnetic levitation trains.
But scientists have previously only been able to create superconducting materials when they are cooled to extremely cold temperatures -- initially, -240 C and more recently about -73 C. Since such cooling is expensive, it has limited applications in the world at large.
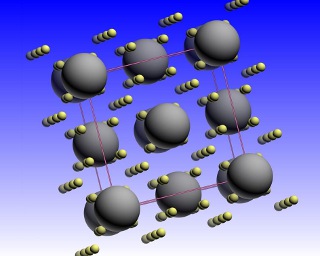
The data from the X-rays allowed scientists to build a model of the crystal structure of the material. [Image courtesy: Drozdov et al]
Recent theoretical predictions have shown that a new class of materials of superconducting hydrides could pave the way for higher temperature superconductivity. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry in Germany teamed up with University of Chicago researchers to create one of these materials, called lanthanum superhydrides, test its superconductivity, and determine its structure and composition.
The only catch was that the material needed to be placed under extremely high pressure -- between 150 and 170 gigapascals, more than one-and-a-half-million times the pressure at sea level. Only under these high-pressure conditions did the material -- a tiny sample only a few microns across -- exhibit superconductivity at the new record temperature.
In fact, the material showed three of the four characteristics needed to prove superconductivity: It dropped its electrical resistance, decreased its critical temperature under an external magnetic field, and showed a temperature change when some elements were replaced with different isotopes. The fourth characteristic, called the Meissner effect, in which the material expels any magnetic field, was not detected. That's because the material is so small that this effect could not be observed, researchers said.
They used the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory, which provides ultra-bright, high-energy X-ray beams that have enabled breakthroughs in everything from better batteries to understanding the Earth's deep interior, to analyze the material. In the experiment, researchers within University of Chicago's Center for Advanced Radiation Sources squeezed a tiny sample of the material between two tiny diamonds to exert the pressure needed, then used the beamline's X-rays to probe its structure and composition.
Because the temperatures used to conduct the experiment are within the normal range of many places in the world, that makes the ultimate goal of room temperature -- or at least 0 degrees Celsius -- seem within reach.
The team is already continuing to collaborate to find new materials that can create superconductivity under more reasonable conditions.
"Our next goal is to reduce the pressure needed to synthesize samples, to bring the critical temperature closer to ambient, and perhaps even create samples that could be synthesized at high pressures, but still superconduct at normal pressures," Prakapenka said. "We are continuing to search for new and interesting compounds that will bring us new, and often unexpected, discoveries."
Read "Superconductivity at 250 K in lanthanum hydride under high pressures." Drozdov et al, Nature, May 23, 2019, here.
Source: University of Chicago
Published May 2019
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
