 |
| August 20, 2019 | Volume 15 Issue 31 |
Electrical/Electronic News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Test equipment advancing to meet rapidly changing market needs
 Although the rise of the IoT, 5G, and advanced automotive electronics markets is instigating rapid changes in technology, test equipment is keeping pace, and not just in extensions to bandwidth specifications or signal resolution. Maureen Lipps, Multicomp Pro Private Label Product Segment Leader, Test and Tools, Newark Electronics, runs through important advances in the industry and its tools.
Although the rise of the IoT, 5G, and advanced automotive electronics markets is instigating rapid changes in technology, test equipment is keeping pace, and not just in extensions to bandwidth specifications or signal resolution. Maureen Lipps, Multicomp Pro Private Label Product Segment Leader, Test and Tools, Newark Electronics, runs through important advances in the industry and its tools.
Read the full article.
Smallest rugged AI supercomputer for avionics
 Aitech Systems has released the A178-AV, the latest iteration of its smallest rugged GPGPU AI super-computers available with the powerful NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier System-on-Module. With its compact size, the A178-AV is the most advanced solution for artificial intelligence (AI), deep learning, and video and signal processing for next-gen avionic platforms.
Aitech Systems has released the A178-AV, the latest iteration of its smallest rugged GPGPU AI super-computers available with the powerful NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier System-on-Module. With its compact size, the A178-AV is the most advanced solution for artificial intelligence (AI), deep learning, and video and signal processing for next-gen avionic platforms.
Learn more.
Touchless angle sensors get CAN SAE J1939 interface
 Novotechnik has added the CAN J1939 interface (developed for heavy-duty vehicles) to its RFC4800 Series of touchless angle sensors measuring angular position up to 360°, turn direction, turns, speed, and operational status. It can provide one or two output channels. It has a longer life and robustness than an optical encoder. It can signal if a sensor needs replacing or average a programmable number of values to output to reduce external noise if present. This is wear-free angle measurement made easy.
Novotechnik has added the CAN J1939 interface (developed for heavy-duty vehicles) to its RFC4800 Series of touchless angle sensors measuring angular position up to 360°, turn direction, turns, speed, and operational status. It can provide one or two output channels. It has a longer life and robustness than an optical encoder. It can signal if a sensor needs replacing or average a programmable number of values to output to reduce external noise if present. This is wear-free angle measurement made easy.
Learn more.
Radar level sensor monitors liquids and powders
 The innovative FR Series non-contact radar level sensor from Keyence has been designed to monitor the level of both liquid and powder in any environment. This sensor features short- and long-range models, as well as chemical and sanitary options to address a wide array of level sensing applications. Works even when obstructions or harsh conditions are present, such as build-up, steam, or turbulence.
The innovative FR Series non-contact radar level sensor from Keyence has been designed to monitor the level of both liquid and powder in any environment. This sensor features short- and long-range models, as well as chemical and sanitary options to address a wide array of level sensing applications. Works even when obstructions or harsh conditions are present, such as build-up, steam, or turbulence.
Learn more.
Raspberry Pi launches $70 AI Kit
 Artificial intelligence (AI) is all the rage, and the makers of Raspberry Pi have created a way for enthusiasts of the single-board computer systems to take part and do a lot of experimenting along the way.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is all the rage, and the makers of Raspberry Pi have created a way for enthusiasts of the single-board computer systems to take part and do a lot of experimenting along the way.
Read the full article.
3D model sharing at Brother Industries cuts rework
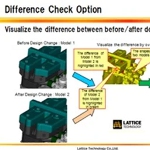 When Brother Industries, maker of printers, computers, and computer-related electronics, deployed Lattice Technology's XVL Player as a viewer for sharing 3D models throughout the processes of product design, parts design, mold design, mold production, and QA of molded parts, they reduced rework significantly -- especially from downstream departments. XVL Studio with its Difference Check Option helped address the rework in mold design, for example, by always keeping everyone informed of design changes.
When Brother Industries, maker of printers, computers, and computer-related electronics, deployed Lattice Technology's XVL Player as a viewer for sharing 3D models throughout the processes of product design, parts design, mold design, mold production, and QA of molded parts, they reduced rework significantly -- especially from downstream departments. XVL Studio with its Difference Check Option helped address the rework in mold design, for example, by always keeping everyone informed of design changes.
Read this real-world case study.
What is 3D-MID? Molded parts with integrated electronics from HARTING
 3D-MID (three-dimensional mechatronic integrated devices) technology combines electronic and mechanical functionalities into a single, 3D component. It replaces the traditional printed circuit board and opens up many new opportunities. It takes injection-molded parts and uses laser-direct structuring to etch areas of conductor structures, which are filled with a copper plating process to create very precise electronic circuits. HARTING, the technology's developer, says it's "Like a PCB, but 3D." Tons of possibilities.
3D-MID (three-dimensional mechatronic integrated devices) technology combines electronic and mechanical functionalities into a single, 3D component. It replaces the traditional printed circuit board and opens up many new opportunities. It takes injection-molded parts and uses laser-direct structuring to etch areas of conductor structures, which are filled with a copper plating process to create very precise electronic circuits. HARTING, the technology's developer, says it's "Like a PCB, but 3D." Tons of possibilities.
Learn more (video included on page).
New! Thermoelectric dehumidifiers for enclosures
 Seifert Systems has just introduced its line of compact Soliflex® Series thermoelectric dehumidifiers, with or without condensate pump. These IP 56-rated units are designed to dehumidify enclosures and small control panels, can be used indoors or outdoors, and are maintenance free. When used with a hygrostat, Soliflex dehumidifiers will keep enclosure humidity below a defined level and only operate when needed.
Seifert Systems has just introduced its line of compact Soliflex® Series thermoelectric dehumidifiers, with or without condensate pump. These IP 56-rated units are designed to dehumidify enclosures and small control panels, can be used indoors or outdoors, and are maintenance free. When used with a hygrostat, Soliflex dehumidifiers will keep enclosure humidity below a defined level and only operate when needed.
Learn more.
More Stego enclosure heater options from AutomationDirect
 Automation-Direct has added more Stego enclosure heaters to their Enclosure Thermal Management lineup. These new 120 to 240 VAC/VDC units include small, flat versions that distribute heat evenly within compact enclosures and are available with 8- or 10-W heating capacities. Also added are compact loop heaters that feature a patented loop body design for increased natural convection airflow, reduced thermal stress on the heater, and better heat transfer. Loop heaters are available in 10- to 150-W heating capacities.
Automation-Direct has added more Stego enclosure heaters to their Enclosure Thermal Management lineup. These new 120 to 240 VAC/VDC units include small, flat versions that distribute heat evenly within compact enclosures and are available with 8- or 10-W heating capacities. Also added are compact loop heaters that feature a patented loop body design for increased natural convection airflow, reduced thermal stress on the heater, and better heat transfer. Loop heaters are available in 10- to 150-W heating capacities.
Learn more.
Great design: Handle with integrated lighting/signaling
 Signaling and indicator lights, switches, and buttons -- elements that hardly any machine can do without. The new JW Winco cabinet U-handle EN 6284 integrates all these functions into a single, compact element. The new U-handle is designed to enhance the operation of systems and machines. It features an integrated button and a large, colored, backlit area on the back of the handle. These elements can be used individually or in combination, providing a versatile tool for system control and process monitoring that can be seen from across the room.
Signaling and indicator lights, switches, and buttons -- elements that hardly any machine can do without. The new JW Winco cabinet U-handle EN 6284 integrates all these functions into a single, compact element. The new U-handle is designed to enhance the operation of systems and machines. It features an integrated button and a large, colored, backlit area on the back of the handle. These elements can be used individually or in combination, providing a versatile tool for system control and process monitoring that can be seen from across the room.
Learn more.
Engineer's Toolbox: What is ground loop feedback?
 Improper grounding can create problems in data logging, data acquisition, and measurement and control systems. One of the most common problems is known as ground loop feedback. Experts at CAS DataLoggers run through five ways to eliminate this problem.
Improper grounding can create problems in data logging, data acquisition, and measurement and control systems. One of the most common problems is known as ground loop feedback. Experts at CAS DataLoggers run through five ways to eliminate this problem.
Read the full article.
AI development kit for multi-camera products
 The QCS6490 Vision-AI Development Kit from Avnet enables engineering teams to rapidly prototype hardware, application software, and AI enablement for multi-camera, high-performance, Edge AI-enabled custom embedded products. The kit facilitates design with the new, energy-efficient MSC SM2S-QCS6490 SMARC compute module based on the Qualcomm QCS6490 processor. Provides support for up to four MIPI CSI cameras and concurrent Mini DisplayPort and MIPI DSI displays.
The QCS6490 Vision-AI Development Kit from Avnet enables engineering teams to rapidly prototype hardware, application software, and AI enablement for multi-camera, high-performance, Edge AI-enabled custom embedded products. The kit facilitates design with the new, energy-efficient MSC SM2S-QCS6490 SMARC compute module based on the Qualcomm QCS6490 processor. Provides support for up to four MIPI CSI cameras and concurrent Mini DisplayPort and MIPI DSI displays.
Learn more.
High-temp cabinet cooler keeps incineration process in business
 An EXAIR client company handles waste treatment on a large ship by operating an incinerator. The area where the incinerator is located gets very hot (over 120° F). This causes failures in the electronics package used to control the incineration process. Since compressed air is readily available, EXAIR's Model HT4225 Cabinet Cooler System is being used to keep the panel cool. It saved the customer from having to replace their control units due to the hot conditions in the incinerator room. Thermostat control is also available, conserving air and operating only when needed to minimize air consumption.
An EXAIR client company handles waste treatment on a large ship by operating an incinerator. The area where the incinerator is located gets very hot (over 120° F). This causes failures in the electronics package used to control the incineration process. Since compressed air is readily available, EXAIR's Model HT4225 Cabinet Cooler System is being used to keep the panel cool. It saved the customer from having to replace their control units due to the hot conditions in the incinerator room. Thermostat control is also available, conserving air and operating only when needed to minimize air consumption.
Learn about EXAIR's huge selection of Cabinet Coolers.
Compact snap-in capacitors for general-purpose applications
 TDK's new EPCOS B43659 series of snap-in aluminum electrolytic capacitors is the next generation of ultra-compact, general-purpose components for voltages of 450 V (DC) featuring an extremely high CV product. It provides the same features and serves the same applications as the previous series but is much more compact. These RoHS-compliant capacitors can be used in a wide range of applications, such as switched-mode power supplies, frequency converters, UPS, medical equipment, and solar inverters.
TDK's new EPCOS B43659 series of snap-in aluminum electrolytic capacitors is the next generation of ultra-compact, general-purpose components for voltages of 450 V (DC) featuring an extremely high CV product. It provides the same features and serves the same applications as the previous series but is much more compact. These RoHS-compliant capacitors can be used in a wide range of applications, such as switched-mode power supplies, frequency converters, UPS, medical equipment, and solar inverters.
Get all the specs.
Conductive Brush Ring overcomes current leakage in EV powertrains
 SKF's new Conductive Brush Ring paves the way to greater reliability and longer life in high-performance electric vehicle powertrain systems. Using pure carbon fiber bristles, it provides a reliable electrical connection between an EV eAxle rotor shaft and its housing. When used in combination with SKF Hybrid ceramic ball bearings, it helps to alleviate parasitic current effects that can lead to premature failure in bearings and other components. Available in different configurations for wet (oil-lubricated) motor designs -- and soon for dry (sealed) applications.
SKF's new Conductive Brush Ring paves the way to greater reliability and longer life in high-performance electric vehicle powertrain systems. Using pure carbon fiber bristles, it provides a reliable electrical connection between an EV eAxle rotor shaft and its housing. When used in combination with SKF Hybrid ceramic ball bearings, it helps to alleviate parasitic current effects that can lead to premature failure in bearings and other components. Available in different configurations for wet (oil-lubricated) motor designs -- and soon for dry (sealed) applications.
Learn more.
Stanford researchers build an effective heat shield just 10 atoms thick to protect electronic devices
This greatly magnified image shows four layers of atomically thin materials that form a heat shield just 2 to 3 nanometers thick, or roughly 50,000 times thinner than a sheet of paper. [Image credit: National Institute of Standards and Technology]
By Tom Abate, Stanford University
Excess heat given off by smartphones, laptops, and other electronic devices can be annoying, but beyond that it contributes to malfunctions and, in extreme cases, can even cause lithium batteries to explode.
To guard against such ills, engineers often insert glass, plastic, or even layers of air as insulation to prevent heat-generating components like microprocessors from causing damage or discomforting users.
Now, Stanford researchers have shown that a few layers of atomically thin materials, stacked like sheets of paper atop hot spots, can provide the same insulation as a sheet of glass 100 times thicker. In the near term, thinner heat shields will enable engineers to make electronic devices even more compact than those we have today, said Eric Pop, professor of electrical engineering and senior author of a paper published Aug. 16 in Science Advances.
"We're looking at the heat in electronic devices in an entirely new way," Pop said.
Detecting sound as heat
The heat we feel from smartphones or laptops is actually an inaudible form of high-frequency sound. If that seems crazy, consider the underlying physics. Electricity flows through wires as a stream of electrons. As these electrons move, they collide with the atoms of the materials through which they pass. With each such collision an electron causes an atom to vibrate, and the more current flows, the more collisions occur, until electrons are beating on atoms like so many hammers on so many bells -- except that this cacophony of vibrations moves through the solid material at frequencies far above the threshold of hearing, generating energy that we feel as heat.
Thinking about heat as a form of sound inspired the Stanford researchers to borrow some principles from the physical world. From his days as a radio DJ at Stanford's KZSU 90.1 FM, Pop knew that music recording studios are quiet thanks to thick glass windows that block the exterior sound. A similar principle applies to the heat shields in today's electronics. If better insulation were their only concern, the researchers could simply borrow the music studio principle and thicken their heat barriers. But that would frustrate efforts to make electronics thinner. Their solution was to borrow a trick from homeowners, who install multi-paned windows -- usually, layers of air between sheets of glass with varying thickness -- to make interiors warmer and quieter.
"We adapted that idea by creating an insulator that used several layers of atomically thin materials instead of a thick mass of glass," said postdoctoral scholar Sam Vaziri, the lead author on the paper.
Atomically thin materials are a relatively recent discovery. It was only 15 years ago that scientists were able to isolate some materials into such thin layers. The first example discovered was graphene, which is a single layer of carbon atoms and, ever since it was found, scientists have been looking for, and experimenting with, other sheet-like materials. The Stanford team used a layer of graphene and three other sheet-like materials -- each three atoms thick -- to create a four-layered insulator just 10 atoms deep. Despite its thinness, the insulator is effective because the atomic heat vibrations are dampened and lose much of their energy as they pass through each layer.
To make nanoscale heat shields practical, the researchers will have to find some mass-production technique to spray or otherwise deposit atom-thin layers of materials onto electronic components during manufacturing. But behind the immediate goal of developing thinner insulators looms a larger ambition: Scientists hope to one day control the vibrational energy inside materials the way they now control electricity and light. As they come to understand the heat in solid objects as a form of sound, a new field of phononics is emerging, a name taken from the Greek root word behind telephone, phonograph, and phonetics.
"As engineers, we know quite a lot about how to control electricity, and we're getting better with light, but we're just starting to understand how to manipulate the high-frequency sound that manifests itself as heat at the atomic scale," Pop said.
Eric Pop is an affiliate of the Precourt Institute for Energy. Stanford authors include former postdoctoral scholars Eilam Yalon and Miguel Muñoz Rojo, and graduate students Connor McClellan, Connor Bailey, Kirby Smithe, Alexander Gabourie, Victoria Chen, Sanchit Deshmukh, and Saurabh Suryavanshi. Other authors are from Theiss Research and the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Published August 2019
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
