 |
| April 21, 2020 | Volume 16 Issue 15 |
Mechanical News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Engineer's Toolbox: How to design the optimum hinge
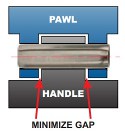 Although many pin styles are available, Coiled Spring Pins are particularly well suited for
use in both friction- and free-fit hinges. To achieve optimum long-term hinge performance,
designers should observe these helpful design guidelines from SPIROL.
Although many pin styles are available, Coiled Spring Pins are particularly well suited for
use in both friction- and free-fit hinges. To achieve optimum long-term hinge performance,
designers should observe these helpful design guidelines from SPIROL.
Read the full article.
Innovative new robo welding gun
 Comau's newest N-WG welding gun is designed for high-speed spot welding for traditional, hybrid, and electric vehicles, in addition to general industry sectors. It features a patented, single-body architecture that enables rapid reconfiguration between welding types and forces, and it delivers consistent performance across a broad range of applications, including steel and (soon) aluminum welding. It supports both X and C standard gun configurations, has fast arm exchange, and universal mounting options. It is fully compatible with major robot brands and represents a significant advancement in spot welding performance and cost efficiency.
Comau's newest N-WG welding gun is designed for high-speed spot welding for traditional, hybrid, and electric vehicles, in addition to general industry sectors. It features a patented, single-body architecture that enables rapid reconfiguration between welding types and forces, and it delivers consistent performance across a broad range of applications, including steel and (soon) aluminum welding. It supports both X and C standard gun configurations, has fast arm exchange, and universal mounting options. It is fully compatible with major robot brands and represents a significant advancement in spot welding performance and cost efficiency.
Learn more.
What's a SLIC Pin®? Pin and cotter all in one!
 The SLIC Pin (Self-Locking Implanted Cotter Pin) from Pivot Point is a pin and cotter all in one. This one-piece locking clevis pin is cost saving, fast, and secure. It functions as a quick locking pin wherever you need a fast-lock function. It features a spring-loaded plunger that functions as an easy insertion ramp. This revolutionary fastening pin is very popular and used successfully in a wide range of applications.
The SLIC Pin (Self-Locking Implanted Cotter Pin) from Pivot Point is a pin and cotter all in one. This one-piece locking clevis pin is cost saving, fast, and secure. It functions as a quick locking pin wherever you need a fast-lock function. It features a spring-loaded plunger that functions as an easy insertion ramp. This revolutionary fastening pin is very popular and used successfully in a wide range of applications.
Learn more.
Engineering challenge: Which 3D-printed parts will fade?
 How does prolonged exposure to intense UV light impact 3D-printed plastics? Will they fade? This is what Xometry's Director of Application Engineering, Greg Paulsen, set to find out. In this video, Paulsen performs comprehensive tests on samples manufactured using various additive processes, including FDM, SLS, SLA, PolyJet, DLS, and LSPc, to determine their UV resistance. Very informative. Some results may surprise you.
How does prolonged exposure to intense UV light impact 3D-printed plastics? Will they fade? This is what Xometry's Director of Application Engineering, Greg Paulsen, set to find out. In this video, Paulsen performs comprehensive tests on samples manufactured using various additive processes, including FDM, SLS, SLA, PolyJet, DLS, and LSPc, to determine their UV resistance. Very informative. Some results may surprise you.
View the video.
Copper filament for 3D printing
 Virtual Foundry, the company that brought us 3D-printable lunar regolith simulant, says its popular Copper Filamet™ (not a typo) is "back in stock and ready for your next project." This material is compatible with any open-architecture FDM/FFF 3D printer. After sintering, final parts are 100% pure copper. Also available as pellets. The company says this is one of the easiest materials to print and sinter. New Porcelain Filamet™ available too.
Virtual Foundry, the company that brought us 3D-printable lunar regolith simulant, says its popular Copper Filamet™ (not a typo) is "back in stock and ready for your next project." This material is compatible with any open-architecture FDM/FFF 3D printer. After sintering, final parts are 100% pure copper. Also available as pellets. The company says this is one of the easiest materials to print and sinter. New Porcelain Filamet™ available too.
Learn more and get all the specs.
Copper foam -- so many advantages
 Copper foam from Goodfellow combines the outstanding thermal conductivity of copper with the structural benefits of a metal foam. These features are of particular interest to design engineers working in the fields of medical products and devices, defense systems and manned flight, power generation, and the manufacture of semiconductor devices. This product has a true skeletal structure with no voids, inclusions, or entrapments. A perennial favorite of Designfax readers.
Copper foam from Goodfellow combines the outstanding thermal conductivity of copper with the structural benefits of a metal foam. These features are of particular interest to design engineers working in the fields of medical products and devices, defense systems and manned flight, power generation, and the manufacture of semiconductor devices. This product has a true skeletal structure with no voids, inclusions, or entrapments. A perennial favorite of Designfax readers.
Learn more.
Full-color 3D-printing Design Guide from Xometry
 With Xometry's PolyJet 3D-printing service, you can order full-color 3D prints easily. Their no-cost design guide will help you learn about different aspects of 3D printing colorful parts, how to create and add color to your models, and best practices to keep in mind when printing in full color. Learn how to take full advantage of the 600,000 unique colors available in this flexible additive process.
With Xometry's PolyJet 3D-printing service, you can order full-color 3D prints easily. Their no-cost design guide will help you learn about different aspects of 3D printing colorful parts, how to create and add color to your models, and best practices to keep in mind when printing in full color. Learn how to take full advantage of the 600,000 unique colors available in this flexible additive process.
Get the Xometry guide.
Tech Tip: How to create high-quality STL files for 3D prints
 Have you ever 3D printed a part that had flat spots or faceted surfaces where smooth curves were supposed to be? You are not alone, and it's not your 3D printer's fault. According to Markforged, the culprit is likely a lack of resolution in the STL file used to create the part.
Have you ever 3D printed a part that had flat spots or faceted surfaces where smooth curves were supposed to be? You are not alone, and it's not your 3D printer's fault. According to Markforged, the culprit is likely a lack of resolution in the STL file used to create the part.
Read this detailed and informative Markforged blog.
Test your knowledge: High-temp adhesives
 Put your knowledge to the test by trying to answer these key questions on how to choose the right high-temperature-resistant adhesive. The technical experts from Master Bond cover critical information necessary for the selection process, including questions on glass transition temperature and service temperature range. Some of the answers may surprise even the savviest of engineers.
Put your knowledge to the test by trying to answer these key questions on how to choose the right high-temperature-resistant adhesive. The technical experts from Master Bond cover critical information necessary for the selection process, including questions on glass transition temperature and service temperature range. Some of the answers may surprise even the savviest of engineers.
Take the quiz.
Engineer's Toolbox: How to pin a shaft and hub assembly properly
 One of the primary benefits of using a coiled spring pin to affix a hub or gear to a shaft is the coiled pin's ability to prevent hole damage. Another is the coiled pin absorbs wider hole tolerances than any other press-fit pin. This translates to lower total manufacturing costs of the assembly. However, there are a few design guidelines that must be adhered to in order to achieve the maximum strength of the pinned system and prevent damage to the assembly.
One of the primary benefits of using a coiled spring pin to affix a hub or gear to a shaft is the coiled pin's ability to prevent hole damage. Another is the coiled pin absorbs wider hole tolerances than any other press-fit pin. This translates to lower total manufacturing costs of the assembly. However, there are a few design guidelines that must be adhered to in order to achieve the maximum strength of the pinned system and prevent damage to the assembly.
Read this very informative SPIROL article.
What's new in Creo Parametric 11.0?
 Creo Parametric 11.0 is packed with productivity-enhancing updates, and sometimes the smallest changes make the biggest impact in your daily workflows. Mark Potrzebowski, Technical Training Engineer, Rand 3D, runs through the newest functionality -- from improved surface modeling tools to smarter file management and model tree navigation. Videos provide extra instruction.
Creo Parametric 11.0 is packed with productivity-enhancing updates, and sometimes the smallest changes make the biggest impact in your daily workflows. Mark Potrzebowski, Technical Training Engineer, Rand 3D, runs through the newest functionality -- from improved surface modeling tools to smarter file management and model tree navigation. Videos provide extra instruction.
Read the full article.
What's so special about wave springs?
 Don't settle for ordinary springs. Opt for Rotor Clip wave springs. A wave spring is a type of flat wire compression spring characterized by its unique waveform-like structure. Unlike traditional coil springs, wave springs offer an innovative solution to complex engineering challenges, producing forces from bending, not torsion. Their standout feature lies in their ability to compress and expand efficiently while occupying up to 50% less axial space than traditional compression springs. Experience the difference Rotor Clip wave springs can make in your applications today!
Don't settle for ordinary springs. Opt for Rotor Clip wave springs. A wave spring is a type of flat wire compression spring characterized by its unique waveform-like structure. Unlike traditional coil springs, wave springs offer an innovative solution to complex engineering challenges, producing forces from bending, not torsion. Their standout feature lies in their ability to compress and expand efficiently while occupying up to 50% less axial space than traditional compression springs. Experience the difference Rotor Clip wave springs can make in your applications today!
View the video.
New Standard Parts Handbook from JW Winco
 JW Winco's printed Standard Parts Handbook is a comprehensive 2,184-page reference that supports designers and engineers with the largest selection of standard parts categorized into three main groups: operating, clamping, and machine parts. More than 75,000 standard parts can be found in this valuable resource, including toggle clamps, shaft collars, concealed multiple-joint hinges, and hygienically designed components.
JW Winco's printed Standard Parts Handbook is a comprehensive 2,184-page reference that supports designers and engineers with the largest selection of standard parts categorized into three main groups: operating, clamping, and machine parts. More than 75,000 standard parts can be found in this valuable resource, including toggle clamps, shaft collars, concealed multiple-joint hinges, and hygienically designed components.
Get your Standard Parts Handbook today.
Looking to save space in your designs?
 Watch Smalley's quick explainer video to see how engineer Frank improved his product designs by switching from traditional coil springs to compact, efficient wave springs. Tasked with making his products smaller while keeping costs down, Frank found wave springs were the perfect solution.
Watch Smalley's quick explainer video to see how engineer Frank improved his product designs by switching from traditional coil springs to compact, efficient wave springs. Tasked with making his products smaller while keeping costs down, Frank found wave springs were the perfect solution.
View the video.
Top die casting design tips
 You can improve the design and cost of your die cast parts with these top tips from Xometry's Joel Schadegg. Topics include: Fillets and Radii, Wall Thicknesses, Ribs and Metal Savers, Holes and Windows, Parting Lines, and more. Follow these recommendations so you have the highest chance of success with your project.
You can improve the design and cost of your die cast parts with these top tips from Xometry's Joel Schadegg. Topics include: Fillets and Radii, Wall Thicknesses, Ribs and Metal Savers, Holes and Windows, Parting Lines, and more. Follow these recommendations so you have the highest chance of success with your project.
Read the full Xometry article.
German scientists identify extremophile microbe that could help degrade polyurethane-based plastics
There may be a small answer to one of the biggest problems on the planet.
German researchers report in the journal Frontiers in Microbiology that they have identified and characterized a strain of bacteria capable of degrading some of the chemical building blocks of polyurethane.
"The bacteria can use these compounds as a sole source of carbon, nitrogen, and energy," said Dr. Hermann J. Heipieper, a senior scientist at the Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research-UFZ in Leipzig, Germany, and co-author of the new paper. "This finding represents an important step in being able to reuse hard-to-recycle PU products."
In 2015, polyurethane products alone accounted for 3.5 million tons of the plastics produced in Europe. Polyurethane is used in everything from refrigerators and buildings to footwear and furniture to numerous other applications that can leverage its lightweight, insulating, and flexible properties.
Unfortunately, polyurethane is difficult and energy intensive to recycle or destroy as most of these kinds of plastics are thermosetting polymers that do not melt when heated. The waste mostly ends up in landfills where it releases a number of toxic chemicals, some of which are carcinogenic.
The use of microorganisms like bacteria and fungi to break down oil-based plastics is an ongoing area of research. However, few studies have addressed biodegradation of polyurethanes like the current paper.
The team out of Germany managed to isolate a bacterium, Pseudomonas sp. TDA1, from a site rich in brittle plastic waste that shows promise in attacking some of the chemical bonds that make up polyurethane plastics.
The researchers performed a genomic analysis to identify the degradation pathways at work. They made preliminary discoveries about the factors that help the microbe metabolize certain chemical compounds in plastic for energy. They also conducted other analyses and experiments to understand the bacterium's capabilities.
This particular strain is part of a group of bacteria that are well known for their tolerance of toxic organic compounds and other forms of stress, according to Dr. Christian Eberlein with the Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research-UFZ. He is a co-author on the paper who coordinated and supervised the work.
"That trait is also named solvent-tolerance and is one form of extremophilic microorganisms," he said.
The research is part of a European Union scientific program dubbed P4SB (From Plastic waste to Plastic value using Pseudomonas putida Synthetic Biology), which is attempting to find useful microorganisms that can bioconvert oil-based plastics into fully biodegradable ones. As the name implies, the project has focused on a bacterium known as Pseudomonas putida.
In addition to polyurethane, the P4SB consortium, which includes the Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research-UFZ, is also testing the efficacy of microbes to degrade plastics made of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is widely used in plastic water bottles.
Heipieper said the first step of any future research on Pseudomonas sp. TDA1 will be to identify the genes that code for the extracellular enzymes that are capable of breaking down certain chemical compounds in polyester-based polyurethanes. Extracellular enzymes, also called exoenzymes, are proteins secreted outside of a cell that cause a biochemical reaction.
However, there is no immediate plan to engineer these or other enzymes using synthetic biology techniques for bioplastic production. That could involve, for instance, genetically converting the bacteria into mini-factories capable of transforming oil-based chemical compounds into biodegradable ones for planet-friendly plastics.
Heipieper said more "fundamental knowledge" like in the current study is needed before scientists can make that technological and commercial leap.
One small step at a time.
Source: Frontiers in Microbiology journal
Published April 2020
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy


